In essence, YAG is the material that makes modern white LED lighting possible. Its full name is Yttrium-Aluminum Garnet, a synthetic crystal that functions as a highly efficient "color converter." Inside a typical white LED, a layer of YAG (doped with cerium) absorbs a portion of the blue light emitted by the LED chip and re-emits it as yellow light. Our eyes perceive this combination of blue and yellow light as white.
The core function of YAG is not to produce light itself, but to transform the color of light from a source. It is the key ingredient that turns the single-color blue light from an LED chip into the useful, efficient white light we use for illumination every day.

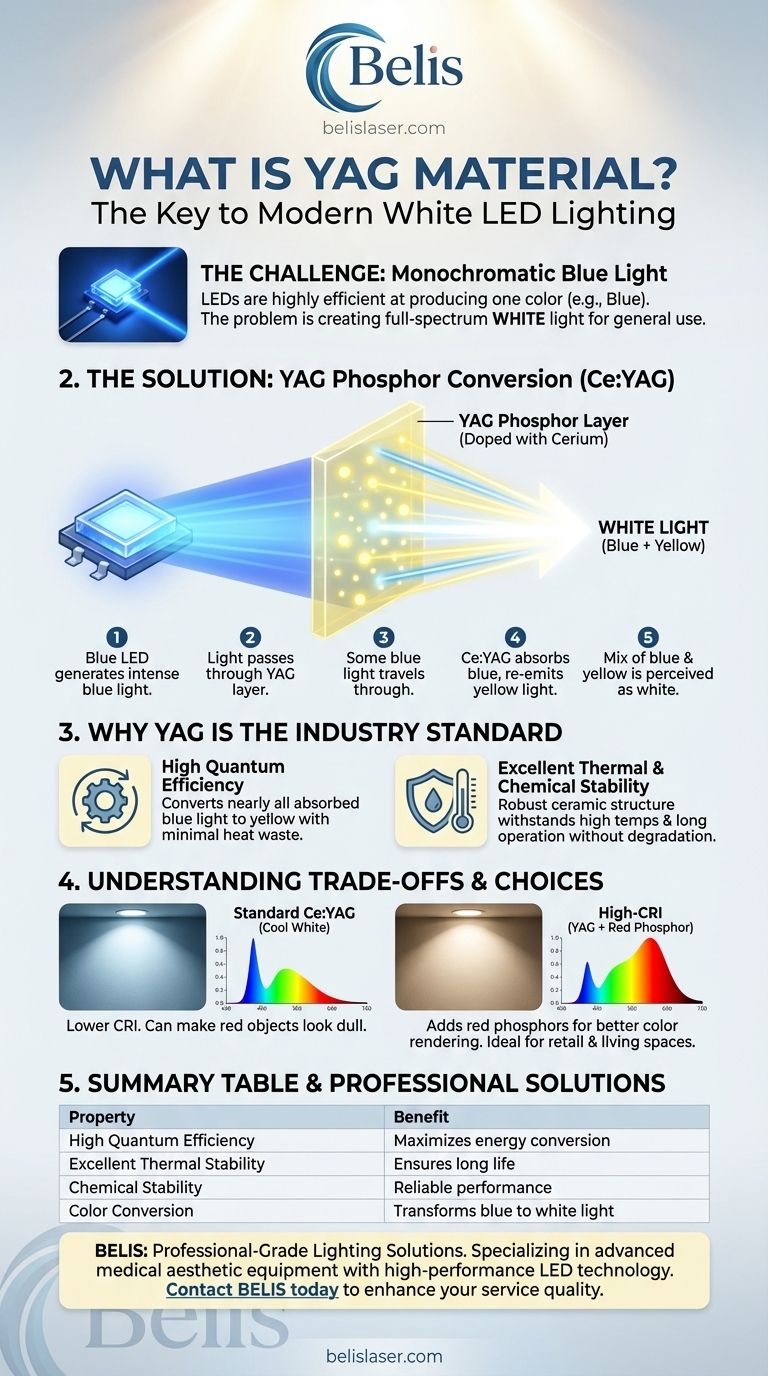
The Challenge: Creating White Light from LEDs
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are inherently monochromatic, meaning they are brilliant at producing a single, specific color of light with very high efficiency.
For decades, the most efficient and commercially viable LEDs have been blue. This presented a fundamental problem for general lighting: how do you create the full-spectrum white light needed to illuminate a room from a single point of blue light?
How YAG Solves the Problem: The Science of Phosphor Conversion
The solution came from a class of materials called phosphors. YAG is the most important and widely used phosphor in the lighting industry.
What is a Phosphor?
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits luminescence—it absorbs energy in one form and re-emits it as light. In an LED, the phosphor absorbs high-energy photons (blue light) and emits lower-energy photons (like yellow or red light).
The Role of Cerium Doping (Ce:YAG)
Pure YAG crystal does not have this property on its own. To activate it, manufacturers introduce a precise impurity into the crystal structure in a process called doping.
When doped with the element cerium (Ce), the material becomes Ce:YAG. This specific formulation is what allows the crystal to very efficiently absorb blue light and re-emit it as a broad band of yellow light.
The Path from Blue to White
The process inside a white LED is remarkably simple and effective:
- A semiconductor chip generates intense blue light.
- This light passes through a thin layer of YAG phosphor coated on or near the chip.
- Some blue light travels straight through the phosphor layer untouched.
- The rest of the blue light is absorbed by the Ce:YAG, which then immediately emits yellow light.
- The mix of the remaining blue light and the new yellow light exits the bulb, and our eyes perceive the combination as white light.
Why YAG is the Industry Standard
While other phosphors exist, YAG became the dominant material for white LEDs due to a unique combination of superior properties.
High Quantum Efficiency
Quantum efficiency refers to how well the material converts absorbed light into emitted light. Ce:YAG is exceptionally efficient, converting nearly all the blue light it absorbs into yellow light with very little energy wasted as heat. This is a primary reason for the high energy efficiency of modern LED bulbs.
Excellent Thermal and Chemical Stability
YAG is a robust ceramic with a stable cubic crystal structure. It can withstand the high temperatures and intense light flux generated inside an LED package for tens of thousands of hours without significant degradation. This stability ensures a long operational life and consistent color over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its advantages, the basic YAG-based approach has inherent limitations that define the quality of the light produced.
The "Cool White" Bias
Because the final output is a simple mix of blue and yellow, the resulting light often has a "cool," bluish tint. Adjusting the thickness of the YAG layer can make the light "warmer" (more yellow), but a basic Ce:YAG system struggles to produce a truly warm, incandescent-like light.
Poor Color Rendering
The most significant trade-off is often a low Color Rendering Index (CRI). Since the light's spectrum has large peaks in the blue and yellow regions but is weak in others (especially red), objects illuminated by this light may appear washed out or have their colors distorted. This is why some early white LEDs made red objects look dull and brownish.
To overcome this, manufacturers of high-quality LEDs add other phosphors, such as red-emitting nitrides, to the YAG mixture to fill in the spectral gaps and produce a fuller, more natural white light.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding YAG's role helps you make more informed decisions when selecting lighting for a specific purpose.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness: Standard LEDs using only a Ce:YAG phosphor are an excellent choice for general-purpose lighting where perfect color accuracy is not critical.
- If your primary focus is accurate color representation (for retail, art, or living spaces): Seek out LEDs advertised as "High-CRI." These almost always use a more advanced phosphor system that builds upon YAG by adding other phosphors to create a more complete and natural light spectrum.
By understanding the function of this critical material, you can see past simple brightness metrics and choose lighting based on the quality and character of the light itself.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for LED Lighting |
|---|---|
| High Quantum Efficiency | Maximizes energy conversion, reducing wasted heat and power consumption. |
| Excellent Thermal Stability | Ensures long life and consistent color output under high temperatures. |
| Chemical Stability | Provides reliable performance over thousands of hours without degradation. |
| Color Conversion | Transforms monochromatic blue light into usable white light for general illumination. |
Need Professional-Grade Lighting Solutions?
BELIS specializes in advanced medical aesthetic equipment, integrating high-performance LED technologies for precise and reliable treatments. Our expertise in stable, efficient light sources ensures optimal results for medical aesthetics clinics and premium beauty salons.
Contact BELIS today to learn how our professional-grade equipment can enhance your service quality and operational efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Clinic Use IPL and SHR Hair Removal Machine with Nd Yag Laser Tattoo Removal
- Pico Picosecond Laser Machine for Tattoo Removal Picosure Pico Laser
- Clinic Use IPL SHR ND YAG Laser Hair Removal RF Skin Tightening Machine
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Trilaser Diode Hair Removal Machine for Beauty Clinic Use
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of Nd:YAG laser? Versatile Power for Industry & Medicine
- How effective is the Q-Switched laser on stubborn tattoo ink colors? Master the Science of Multi-Color Removal
- How many sessions are required for tattoo removal with a neodymium YAG laser? Your Guide to Results and Recovery
- How does an Nd:YAG laser generally operate? Unlock High-Energy Precision for Deep-Tissue Laser Treatments
- Why is the use of long-pulse Nd:YAG lasers necessary for deep acne? Penetrate & Clear Stubborn Nodules Effectively
- What are the key design considerations for achieving high pulse energies in Q-switched lasers? Optimize Your Laser Power
- Does YAG laser improve skin? Yes, it can rejuvenate, resurface, and tighten your skin.
- How does an Nd:YAG laser function? The Science of Precision Solid-State Skin Treatments



















