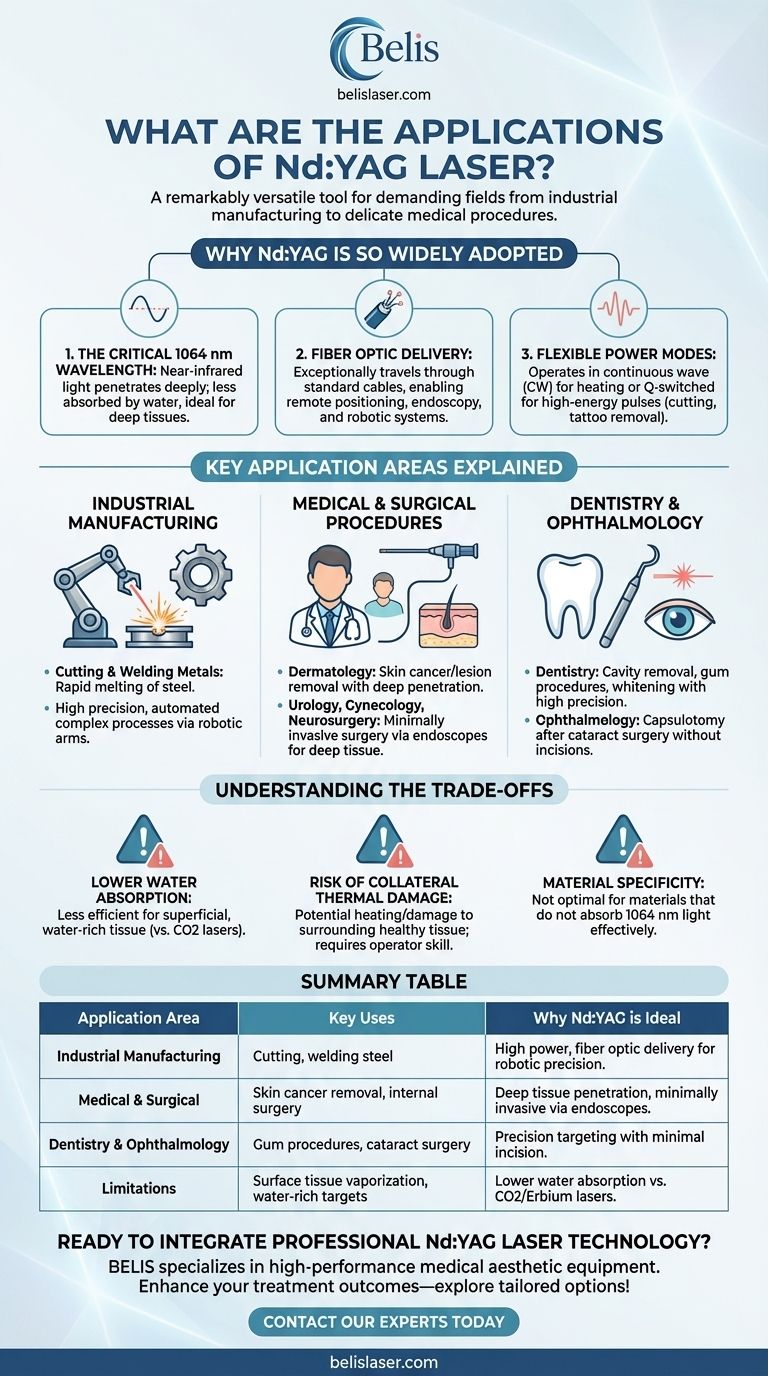
At its core, the Nd:YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet) laser is a remarkably versatile tool used across a vast range of demanding fields. Its applications span heavy industrial manufacturing, such as cutting and welding steel, to delicate medical procedures including skin cancer removal, general surgery, and dentistry.
The Nd:YAG laser's power lies in its specific 1064 nm wavelength. This near-infrared light penetrates deeply into materials and biological tissues and can be efficiently transmitted through fiber optic cables, making it uniquely adaptable for both high-power industrial work and minimally invasive internal surgery.

Why Nd:YAG is So Widely Adopted
The utility of the Nd:YAG laser is not accidental; it stems from a few key physical properties that make it a uniquely flexible solution for very different problems.
The Critical 1064 nm Wavelength
The light produced by an Nd:YAG laser has a wavelength of 1064 nanometers (nm). This places it in the near-infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, invisible to the human eye.
This specific wavelength is not highly absorbed by water, which is a primary component of biological tissue. This allows the laser energy to travel deeper before it is absorbed, a crucial feature for treating structures beneath the skin's surface.
Fiber Optic Delivery
The 1064 nm wavelength travels exceptionally well through standard silica fiber optic cables. This is a game-changing characteristic.
It allows the laser source to be positioned far away from the work area, with the energy delivered precisely to a target via a flexible, maneuverable cable. This is the enabling technology for its use in endoscopy and robotic manufacturing.
Flexible Power Modes
Nd:YAG lasers can be operated in a continuous wave (CW) mode, delivering a steady beam of energy for tasks like heating or coagulation.
They can also be Q-switched to produce extremely short, high-energy pulses. This pulsed mode is essential for applications like cutting, drilling, and tattoo removal, where a powerful ablative force is needed.
Key Application Areas Explained
The physical principles of the Nd:YAG laser translate directly into its broad range of applications.
Industrial Manufacturing
For cutting and welding metals like steel, the Nd:YAG laser's high power can rapidly melt and vaporize the material. When coupled with a robotic arm via fiber optics, it allows for precise, automated, and complex manufacturing processes.
Medical & Surgical Procedures
The laser's ability to penetrate tissue and be delivered via fiber makes it a cornerstone of modern medicine.
It is used widely in dermatology to remove skin cancers and lesions. Its deep penetration targets the underlying structures without requiring significant surface incisions.
In fields like urology, gynecology, and neurosurgery, the laser is passed through an endoscope to coagulate bleeding or ablate tissue in hard-to-reach areas, enabling minimally invasive surgery.
Dentistry and Ophthalmology
In dental surgery, the Nd:YAG can be used to remove decay, perform gum procedures, and whiten teeth with high precision.
Perhaps one of its most well-known uses is in ophthalmology. After cataract surgery, a thin membrane behind the new lens can become cloudy. An Nd:YAG laser can create a tiny opening in this membrane (a capsulotomy) without making any incision into the eye itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single tool is perfect for every job. The properties that make the Nd:YAG laser so useful also create limitations.
Lower Water Absorption
While deep penetration is an advantage, the low absorption by water makes it less efficient than other lasers (like the CO2 laser) for vaporizing superficial, water-rich tissue. The choice of laser depends on whether the target is on the surface or deep within the tissue.
Risk of Collateral Thermal Damage
Because the energy is deposited over a larger, deeper volume, there is a risk of heating and damaging surrounding healthy tissue. This requires significant skill and control from the operator to mitigate.
Material Specificity
While excellent for steel and certain biological targets, the Nd:YAG laser is not the optimal choice for all materials. Materials that do not effectively absorb 1064 nm light may be better served by lasers operating at different wavelengths.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding which laser to use requires matching the tool's properties to the specific objective.
- If your primary focus is high-power, automated metal cutting: The Nd:YAG (or more commonly today, its successor the fiber laser) is ideal due to its power and compatibility with robotic delivery systems.
- If your primary focus is minimally invasive internal surgery: The Nd:YAG's ability to be delivered via flexible endoscopes for deep tissue coagulation is its defining advantage.
- If your primary focus is precise vaporization of surface tissue: A laser with higher water absorption, like a CO2 or Erbium laser, is often a more efficient and safer choice.
- If your primary focus is targeting structures deep inside a transparent medium (like the eye): The Nd:YAG's ability to focus its energy precisely at a distance is unmatched.
Ultimately, mastering the application of an Nd:YAG laser comes from a deep understanding of how its fundamental physics solve a specific real-world problem.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Why Nd:YAG is Ideal |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Manufacturing | Cutting, welding steel | High power, fiber optic delivery for robotic precision |
| Medical & Surgical | Skin cancer removal, internal surgery | Deep tissue penetration, minimally invasive via endoscopes |
| Dentistry & Ophthalmology | Gum procedures, cataract surgery | Precision targeting with minimal incision |
| Limitations | Surface tissue vaporization, water-rich targets | Lower water absorption vs. CO2/Erbium lasers |
Ready to integrate professional Nd:YAG laser technology into your practice? BELIS specializes in high-performance medical aesthetic equipment, delivering reliable, deep-penetrating solutions for medical aesthetics clinics and premium beauty salons. Enhance your treatment outcomes with our advanced laser systems—contact our experts today to explore tailored options!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Q Switch Nd Yag Laser Machine Tattoo Removal Nd Yag Machine
- Clinic Use IPL and SHR Hair Removal Machine with Nd Yag Laser Tattoo Removal
- 7D 12D 4D HIFU Machine Device
- Clinic Diode Laser Hair Removal Machine with SHR and Trilaser Technology
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
People Also Ask
- What types of pigmented lesions can an Nd:YAG laser treat? Expert Skin Solutions for Clinics
- Why is the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser essential for treating PIH? The Gold Standard for Safe Pigment Removal
- What are Q-switched lasers commonly used for? Remove Tattoos & Pigment with Precision
- What is the clinical significance of perifollicular erythema in Nd:YAG hair removal? Your Guide to Treatment Efficacy
- Is Q Switched Nd:YAG laser good? The Gold Standard for Tattoo & Pigment Removal



















