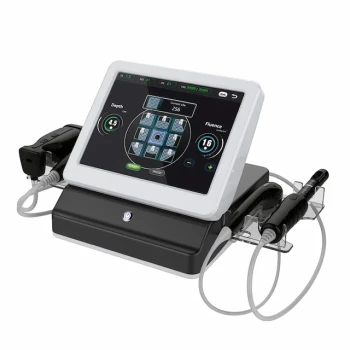
At its core, ultrasound interacts with your body by causing micro-vibrations within your tissues. These high-frequency sound waves create a gentle heating effect, which in turn increases blood flow to the targeted area. This enhanced circulation delivers more oxygen and essential nutrients, which can accelerate the natural healing process for damaged tissue.
The fundamental effect of ultrasound on the body is mechanical and thermal. By transferring sound energy into the tissue, it can be used at low intensity to create images for diagnosis or at higher intensity to stimulate healing for therapy.

The Core Mechanism: From Sound to Cellular Action
Ultrasound's effects are rooted in basic physics. A device called a transducer converts electrical energy into high-frequency sound waves, directing them into the body. How your body's cells react to this energy is what produces the biological effect.
Mechanical Vibration
The sound waves are, in essence, physical pressure waves. As they travel through your body, they cause the cells and molecules in their path to vibrate rapidly. This is the primary mechanical effect of ultrasound.
Thermal Effects (Heating)
This constant, high-speed vibration creates friction between the molecules in the tissue. Just like rubbing your hands together creates warmth, this molecular friction generates a small but significant amount of heat deep within the targeted area.
Increased Blood Flow
The body responds to this slight increase in temperature by dilating the blood vessels in the area, a process known as vasodilation. Wider vessels allow more blood to flow through. This increased circulation is a key objective, especially in therapeutic applications.
The Healing Response
Increased blood flow acts as a catalyst for healing. The fresh, oxygen-rich blood brings the necessary proteins and chemicals that your body uses to repair damaged tissues, like muscles or tendons, more efficiently.
Two Sides of the Same Coin: Diagnostic vs. Therapeutic
It's critical to understand that the term "ultrasound" is used for two very different medical purposes, distinguished primarily by the intensity of the energy used.
Diagnostic Ultrasound (Imaging)
This is the most common use of ultrasound, such as in pregnancy scans or imaging internal organs. It uses very low-intensity waves. The goal here is not to heat or change the tissue, but to listen for the "echoes" as the sound waves bounce off different structures. A computer then translates these echoes into a real-time image.
Therapeutic Ultrasound (Treatment)
Used frequently in physical therapy, this form of ultrasound uses a higher, more focused intensity. The primary goal is to intentionally generate the heating and circulatory effects described above to treat soft tissue injuries, reduce inflammation, and accelerate healing.
Understanding the Safety and Trade-offs
The safety of ultrasound is directly tied to its intensity, duration, and the specific application it's being used for.
The Critical Role of "Dose"
Like any medical treatment, the "dose"—a combination of energy intensity and exposure time—is crucial. Medical ultrasound equipment is precisely calibrated and operated by trained professionals to deliver a specific dose that is effective for its purpose without causing harm.
Why It Is Considered Very Safe
For diagnostic imaging, the energy levels are so low that there are no known long-term harmful effects, which is why it is the preferred method for monitoring pregnancies. In therapeutic use, the controlled heating is localized and designed to stay well within a safe physiological range, avoiding any damage to tissues.
What This Means for You
Understanding the purpose of your specific ultrasound procedure helps clarify its effect on your body.
- If you are undergoing a diagnostic scan (like an organ or pregnancy check): The primary effect is the harmless reflection of low-energy sound waves to create a picture, with no significant impact on your tissue.
- If you are receiving therapeutic ultrasound (for an injury): The goal is to intentionally use focused sound energy to gently heat tissue, increase blood flow, and support your body's own repair mechanisms.
- If you have any safety concerns: Always ensure your procedure is performed by a qualified and licensed medical professional who can ensure the equipment is used correctly for its intended purpose.
Ultimately, ultrasound is a versatile medical tool that leverages the physics of sound to either see inside the body or help it heal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Diagnostic Ultrasound | Therapeutic Ultrasound |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Create images (e.g., pregnancy scans) | Heal tissue (e.g., muscle injuries) |
| Intensity | Very Low | Higher, Focused |
| Primary Effect | Harmless reflection of sound waves | Gentle heating & increased blood flow |
| Common Use | Monitoring, Examination | Physical Therapy, Rehabilitation |
Ready to integrate professional ultrasound technology into your practice? BELIS specializes in high-precision medical aesthetic equipment, empowering clinics and premium salons with advanced tools for effective therapeutic treatments. Enhance your service offerings and patient outcomes with our reliable technology. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 12D HIFU Machine Device for Facial HIFU Treatment
- 7D 12D 4D HIFU Machine Device
- 9D 7D HIFU Vaginal RF Lifting Treatment
- 22D HIFU Machine Device Facial Machine
- IPL SHR+Radio frecuency machine
People Also Ask
- What are the expected visual results from a HIFU treatment? Discover the Path to Natural Lifting & Contouring
- Which specific areas of the face and body can be treated with HIFU? Full Contouring Guide
- What specific aesthetic concerns can be addressed by ultrasound skin tightening? Lift Jowls & Smooth Neck Creases
- How many HIFU facial sessions are generally required? Get the Best Results for Your Skin Tightening Journey
- What is the average cost of a nonsurgical skin-tightening procedure like HIFU? Budget Guide for Clinics