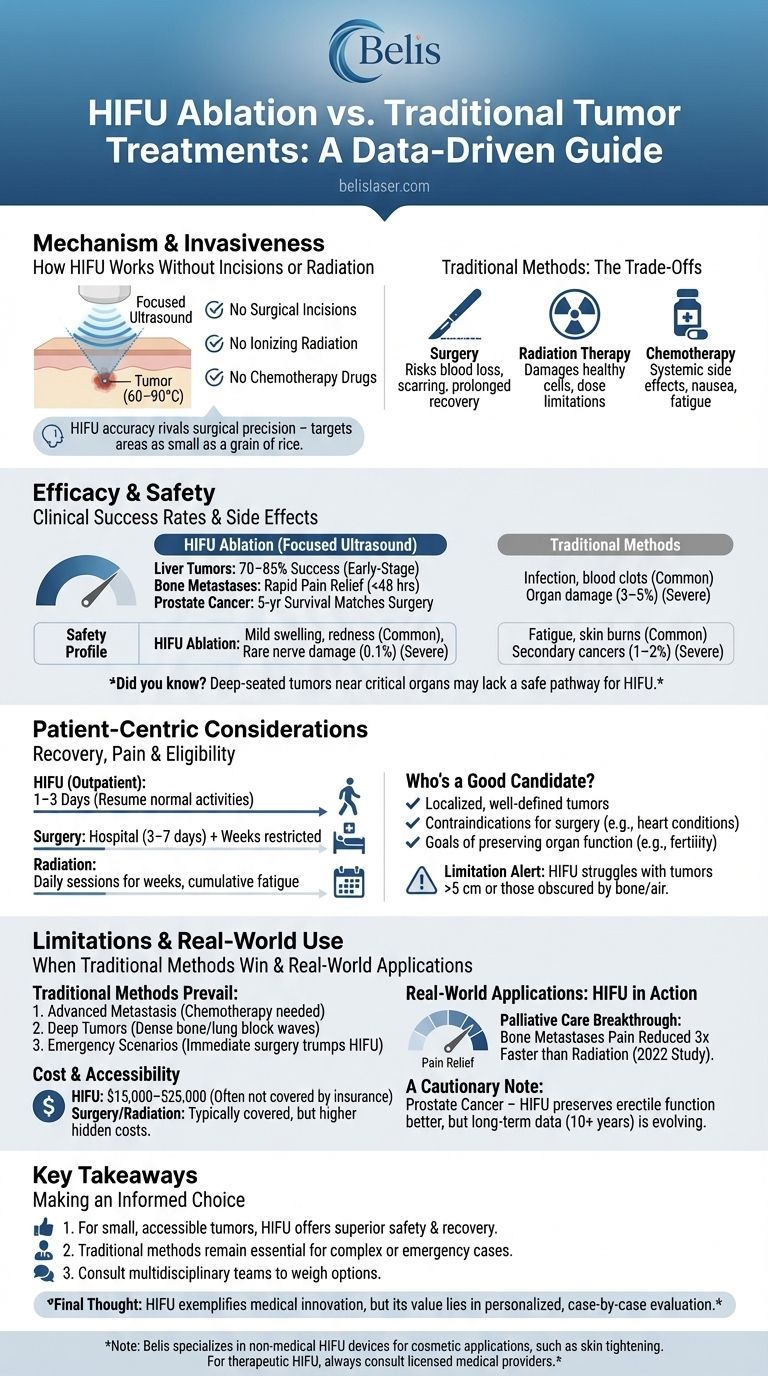
When facing tumor treatment decisions, patients and clinicians increasingly consider High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) ablation as a minimally invasive alternative to surgery or radiation. But how does it truly compare? This evidence-based guide examines HIFU’s mechanism, clinical outcomes, and practical considerations—helping you evaluate its suitability for specific cases.
Mechanism and Invasiveness: How HIFU Works Without Incisions or Radiation
The Science Behind HIFU’s Precision
HIFU destroys tumors using focused ultrasound waves that heat target tissues to 60–90°C without damaging surrounding structures. Unlike traditional methods, it requires:
- No surgical incisions (reducing infection risks)
- No ionizing radiation (eliminating cumulative toxicity concerns)
- No chemotherapy drugs (avoiding systemic side effects)
Did you know? HIFU’s accuracy rivals surgical precision—its ultrasound beams can target areas as small as a grain of rice.
Traditional Methods: The Trade-Offs
- Surgery: Effective for large tumors but risks blood loss, scarring, and prolonged recovery.
- Radiation Therapy: Damages both cancerous and healthy cells over time, with dose limitations.
- Chemotherapy: Affects the entire body, causing nausea, fatigue, and immunosuppression.
Efficacy and Safety: Clinical Success Rates and Side Effects
HIFU’s Track Record
- Liver Tumors: 70–85% success rate in early-stage cases (source: clinical studies), comparable to surgery but with fewer complications.
- Bone Metastases: Provides rapid pain relief (within 48 hours) versus weeks for radiation.
- Prostate Cancer: 5-year survival rates match surgery, with lower incontinence risks.
Safety Profile
| Treatment | Common Side Effects | Severe Risks |
|---|---|---|
| HIFU Ablation | Mild swelling, redness | Rare nerve damage (0.1%) |
| Surgery | Infection, blood clots | Organ damage (3–5%) |
| Radiation | Fatigue, skin burns | Secondary cancers (1–2%) |
Ever wondered why some hospitals still prefer surgery? Deep-seated tumors near critical organs (e.g., brainstem) may lack a safe acoustic pathway for HIFU.
Patient-Centric Considerations: Recovery, Pain, and Eligibility
Recovery Time Comparison
- HIFU: Outpatient procedure; most resume normal activities in 1–3 days.
- Surgery: Hospitalization (3–7 days) + weeks of restricted movement.
- Radiation: Daily sessions for weeks, with cumulative fatigue.
Who’s a Good Candidate?
HIFU suits patients with:
✔ Localized, well-defined tumors (e.g., uterine fibroids, prostate cancer)
✔ Contraindications for surgery (e.g., heart conditions)
✔ Goals of preserving organ function (e.g., fertility-sparing treatments)
Limitation Alert: HIFU struggles with tumors >5 cm or those obscured by bone/air (e.g., lung lesions).
Limitations and Challenges: When Traditional Methods Win
Cases Where Surgery/Radiation Prevail
- Advanced Metastasis: Systemic treatments (chemotherapy) may be unavoidable.
- Deep Tumors: HIFU’s ultrasound waves can’t penetrate dense bone or lung tissue effectively.
- Emergency Scenarios: Immediate surgery trumps HIFU’s planning requirements.
Cost and Accessibility
- HIFU: $15,000–$25,000 (often not covered by insurance outside oncology).
- Surgery/Radiation: Typically covered but higher hidden costs (e.g., rehab, missed work).
Real-World Applications: HIFU in Action
Palliative Care Breakthrough
For bone metastases, HIFU reduces pain 3x faster than radiation, per a 2022 Journal of Clinical Oncology study. Patients report improved quality of life without repeated hospital visits.
A Cautionary Note: Prostate Cancer
While HIFU preserves erectile function better than surgery, long-term data (10+ years) is still evolving. Some urologists recommend it only for low-risk cases.
Key Takeaways: Making an Informed Choice
- For small, accessible tumors, HIFU offers superior safety and recovery over surgery/radiation.
- Traditional methods remain essential for complex or emergency cases.
- Consult multidisciplinary teams—oncologists, surgeons, and HIFU specialists—to weigh options.
Final Thought: HIFU exemplifies how medical innovation can shift paradigms, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its true value lies in personalized, case-by-case evaluation.
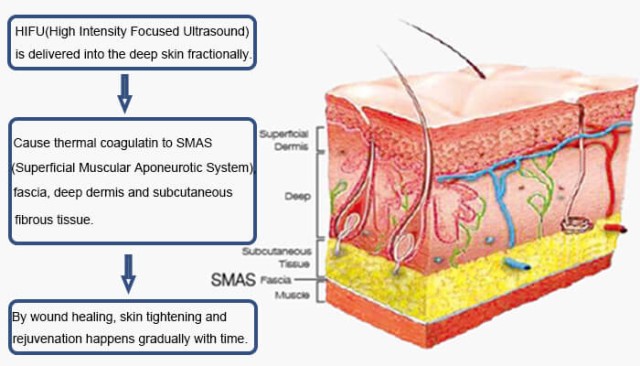
Note: Belis specializes in non-medical HIFU devices for cosmetic applications, such as skin tightening. For therapeutic HIFU, always consult licensed medical providers.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 12D HIFU Machine Device for Facial HIFU Treatment
- 7D 12D 4D HIFU Machine Device
- 4D 12D HIFU Machine Device for Skin Tightening and Lifting
- IPL SHR+Radio frecuency machine
- EMS Body Sculpting Machine for Body Slimming and Sculpting
Related Articles
- How HIFU Triggers Natural Collagen Production for Younger-Looking Skin
- How HIFU Delivers Safer, Smarter Anti-Aging Results: Science-Backed Insights
- HIFU Vaginal Tightening: A Safe and Effective Solution for Vaginal Rejuvenation
- Why HIFU Outperforms Other Non-Surgical Treatments for Lasting Facial Rejuvenation
- HIFU Treatment Explained: The Science Behind Superior Skin Tightening