By far, the most common application of the Nd:YAG laser is in the field of ophthalmology. This solid-state laser is a cornerstone of modern eye care, used for precise, non-invasive procedures that restore vision and manage disease.
The Nd:YAG laser's value comes from its unique ability to pass harmlessly through the clear structures of the eye and deliver a highly focused burst of energy to a precise internal target. This creates a tiny, mechanical disruption that can cut or clear tissue without the need for a surgical incision.
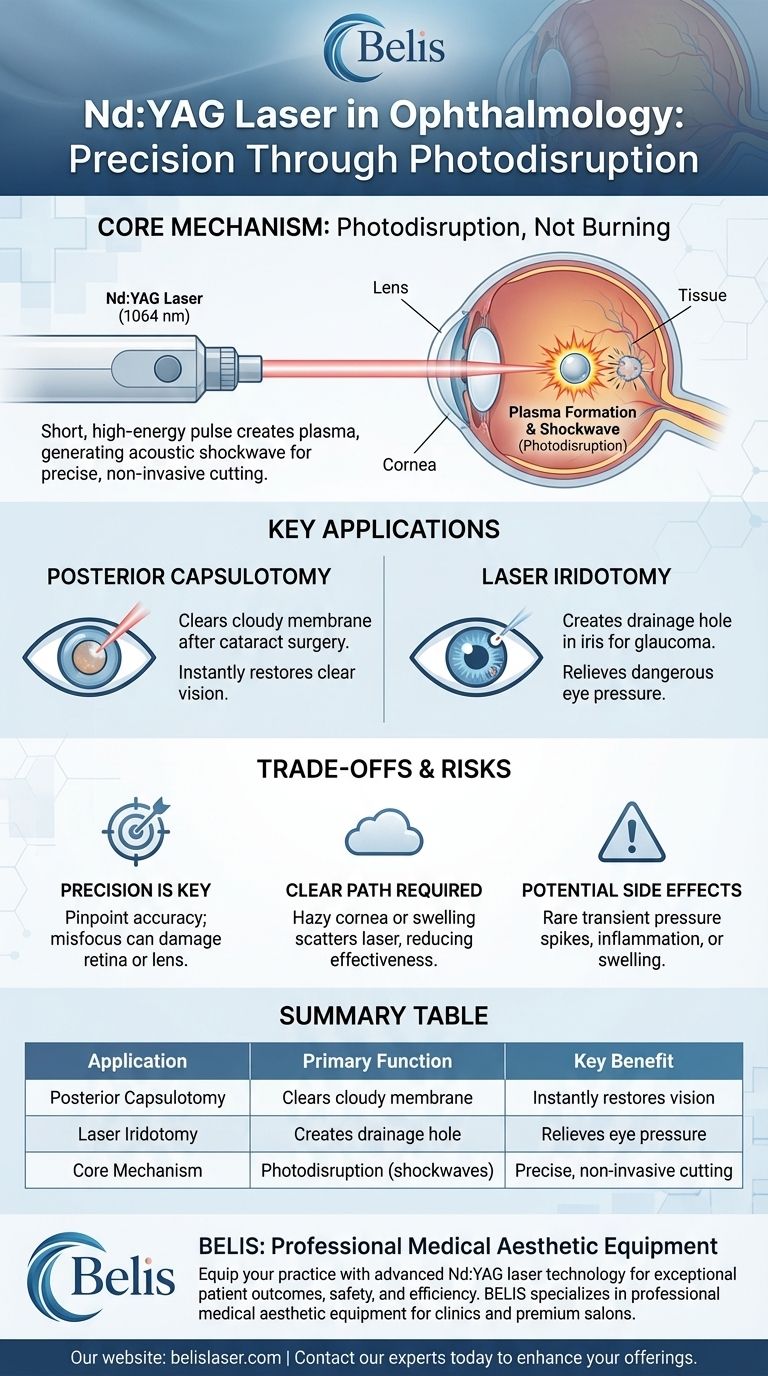
The Core Mechanism: Understanding Photodisruption
The Nd:YAG laser's function is not based on burning or vaporizing tissue, which is a common misconception. Instead, it relies on a sophisticated physical principle known as photodisruption.
A Solid-State Laser with a Specific Wavelength
The "Nd:YAG" name refers to its components: neodymium (Nd) ions are doped into a crystal of yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG). This crystal acts as the laser medium.
This combination produces a laser beam with a wavelength of 1064 nm. This is in the near-infrared part of the spectrum, which is invisible to the human eye and, crucially, passes through the clear cornea and lens without being absorbed.
How Photodisruption Works
When the laser is fired, it delivers an extremely short, high-energy pulse to a tiny, precise focal point.
This intense energy instantly strips electrons from atoms in the tissue, creating a superheated state of matter called plasma.
The plasma bubble expands and collapses in a nanosecond, generating an acoustic shockwave. This rapid mechanical expansion is what cuts or disrupts the targeted tissue, like a microscopic scalpel.
Key Applications in Ophthalmology
The principle of photodisruption makes the Nd:YAG laser ideal for delicate procedures inside the eye, where a physical incision would be highly invasive.
Posterior Capsulotomy
This is the most frequent use of the Nd:YAG laser. After cataract surgery, the thin membrane behind the new intraocular lens, called the posterior capsule, can become cloudy over time, blurring vision.
The surgeon uses the Nd:YAG laser to create a small, clear opening in the center of this cloudy capsule, instantly restoring a clear path for light to reach the retina. The procedure is painless and takes only a few minutes in an office setting.
Laser Iridotomy
For patients with or at risk of angle-closure glaucoma, the Nd:YAG laser can be sight-saving.
The surgeon creates a tiny hole in the iris (the colored part of the eye). This allows built-up fluid to drain properly, relieving the dangerously high intraocular pressure that characterizes this form of glaucoma.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While incredibly effective and safe, the technology is not without its limitations and requires immense skill to operate.
Precision is a Double-Edged Sword
The laser's pinpoint accuracy is its greatest strength. However, if it is not focused correctly, the photodisruptive energy can inadvertently damage other sensitive structures, such as the retina or the implanted lens itself. The skill of the ophthalmologist is paramount.
A Clear Path is Required
The laser beam must have a clear optical path to the target. If the cornea or other parts of the eye are too hazy or swollen, the laser energy can be scattered, making the procedure ineffective or unsafe.
Potential Side Effects
Though rare, the procedure can cause a temporary spike in intraocular pressure, inflammation, or retinal swelling. These complications are typically transient and manageable with medication.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the Nd:YAG laser's role helps clarify its impact on modern medicine and patient care.
- If your primary focus is on medical technology: Recognize the Nd:YAG laser as a prime example of performing "surgery" with light, using a physical force (photodisruption) to achieve a result without an incision.
- If your primary focus is on patient outcomes: This laser represents a minimally invasive tool that can restore vision or prevent blindness in a matter of minutes with minimal discomfort and rapid recovery.
- If your primary focus is on safety principles: Appreciate that its effectiveness is tied directly to the precise delivery of energy, making operator skill and proper patient selection the most critical factors for success.
Ultimately, the Nd:YAG laser has transformed eye care by enabling surgeons to resolve complex internal issues with unparalleled precision and safety.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Posterior Capsulotomy | Clears a cloudy membrane after cataract surgery | Instantly restores clear vision |
| Laser Iridotomy | Creates a drainage hole in the iris for glaucoma | Relieves dangerous eye pressure |
| Core Mechanism | Uses photodisruption (shockwaves) | Precise, non-invasive tissue cutting |
BELIS specializes in professional medical aesthetic equipment, serving medical aesthetics clinics and premium beauty salons.
Equip your practice with the precision and reliability of advanced laser technology. Our Nd:YAG laser systems are designed to deliver exceptional patient outcomes with safety and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discover how our solutions can enhance your service offerings and grow your business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Q Switch Nd Yag Laser Machine Tattoo Removal Nd Yag Machine
- Clinic Use IPL and SHR Hair Removal Machine with Nd Yag Laser Tattoo Removal
- 7D 12D 4D HIFU Machine Device
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- 22D HIFU Machine Device Facial Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the clinical significance of perifollicular erythema in Nd:YAG hair removal? Your Guide to Treatment Efficacy
- Is Q Switched Nd:YAG laser good? The Gold Standard for Tattoo & Pigment Removal
- What advantage does a 7mm spot size provide for Melasma treatment? Maximize Depth and Safety with Nd:YAG Lasers
- How does the Nd:YAG laser work? Unlocking Deep-Tissue Precision for Medical Aesthetics
- Why is the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser essential for treating PIH? The Gold Standard for Safe Pigment Removal



















