While several types of lasers are mainstays in medicine, the CO2 laser is arguably the most common and versatile surgical laser in use today. Its utility is closely followed by other critical technologies like the Nd:YAG laser. The prevalence of a specific laser is directly tied to how its unique wavelength interacts with biological tissue to achieve a desired medical outcome.
The most "common" medical laser is not a single device, but rather a category defined by the intended medical application. The choice between a CO2, Nd:YAG, or another laser type is a deliberate decision based on whether the goal is precise cutting, deep coagulation, or targeting a specific pigment.

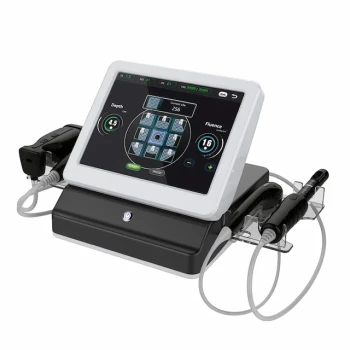
How Wavelength Dictates a Laser's Medical Function
The core principle behind any medical laser is selective photothermolysis. This means using a specific wavelength of light that is strongly absorbed by a target molecule in the body, known as a chromophore.
The Primary Targets in Tissue
The three most important chromophores in medical laser applications are water, hemoglobin (in red blood cells), and melanin (pigment). A laser's effectiveness is determined almost entirely by which of these molecules absorbs its energy.
Wavelength as the Deciding Factor
The laser's wavelength is the physical property that determines which chromophore will absorb its energy most efficiently. A wavelength highly absorbed by water will have a dramatically different effect on tissue than one absorbed by hemoglobin. This is the fundamental concept that separates the different types of medical lasers.
A Profile of the Major Laser Workhorses
Different medical procedures require different tools. The CO2 and Nd:YAG lasers have become staples because their properties are ideally suited for the most common surgical needs: cutting and coagulation.
The CO2 Laser: The Surgical Scalpel
The CO2 laser emits light at a 10,600 nm wavelength. This energy is intensely and rapidly absorbed by water, which constitutes 70-90% of soft tissue.
This immediate absorption causes the water in the cells to flash into steam, instantly vaporizing the tissue in a very precise layer. This makes the CO2 laser an exceptional tool for clean, bloodless cutting, ablation, and vaporization of tissue in fields like dermatology, gynecology, and ENT surgery.
The Nd:YAG Laser: The Deep Coagulator
The Nd:YAG laser uses a 1064 nm wavelength. This energy is poorly absorbed by water but is absorbed by hemoglobin and melanin, allowing the light to penetrate much deeper into tissue before its energy is released.
Instead of instantly vaporizing the surface, this deeper energy deposition gently heats a larger volume of tissue. This makes the Nd:YAG laser ideal for deep tissue coagulation (stopping bleeding), treating vascular lesions, and certain procedures in ophthalmology and oncology where deep thermal effects are desired.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Precision vs. Penetration
No single laser is perfect for every task. The choice always involves a trade-off, primarily between the precision of the cut and the ability to control bleeding in deeper tissue.
The Impact of Water Absorption
The CO2 laser's high absorption by water provides unmatched precision, as its energy is deposited in a very shallow, predictable zone. This minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
The downside is that its ability to stop bleeding (hemostasis) is limited to very small blood vessels at the surface. It cannot reach and coagulate larger, deeper vessels effectively.
The Need for Deeper Coagulation
The Nd:YAG laser's lower water absorption allows it to penetrate and seal larger blood vessels beneath the surface. This superior coagulation comes at the cost of precision. The energy spreads out more, creating a larger zone of thermal effect and making it unsuitable for fine, delicate cuts.
Making the Right Choice for the Goal
The selection of a medical laser is a direct function of the clinical objective. Understanding the target tissue and the desired outcome is the only way to select the appropriate tool.
- If your primary focus is precise tissue cutting or surface vaporization: The CO2 laser is the standard due to its high water absorption, providing clean ablation with minimal collateral thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is deep tissue coagulation or shrinking tissue: The Nd:YAG laser is the superior choice for its ability to penetrate tissue and deliver thermal energy to a larger volume.
- If your primary focus is targeting specific pigments like blood vessels or tattoos: Specialized lasers like the Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL) or KTP laser, which have wavelengths highly specific to hemoglobin, are required.
Ultimately, a medical laser's power lies in matching its specific wavelength to the correct biological target.
Summary Table:
| Laser Type | Wavelength | Primary Chromophore | Key Medical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser | 10,600 nm | Water | Precise cutting, ablation, and vaporization of soft tissue |
| Nd:YAG Laser | 1,064 nm | Hemoglobin & Melanin | Deep tissue coagulation and treatment of vascular lesions |
Ready to Integrate the Right Medical Laser into Your Practice?
Choosing between a CO2 laser for precision or an Nd:YAG for deep coagulation is critical for your clinical outcomes. BELIS specializes in providing professional medical aesthetic equipment, helping medical aesthetics clinics and premium beauty salons enhance their service offerings with the right technology.
Let our experts guide you to the perfect laser solution for your specific needs. Contact BELIS today for a personalized consultation and discover how our advanced equipment can drive your practice's growth and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Fractional CO2 Laser Machine for Skin Treatment
- Fractional CO2 Laser Machine for Skin Treatment
- Q Switch Nd Yag Laser Machine Tattoo Removal Nd Yag Machine
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Multifunctional Laser Hair Growth Machine Device for Hair Growth
People Also Ask
- How often should you do fractional CO2 laser? The 4-6 Week Rule for Optimal Results
- What is a fractional CO2 laser machine used for? A Guide to Advanced Skin Resurfacing
- Who is not a good candidate for CO2 laser? Avoid Complications and Ensure Safe Treatment
- What does a CO2 laser do to your face? Achieve Profound Skin Resurfacing & Renewal
- How does fractional CO2 laser work? The Science Behind Powerful Skin Renewal