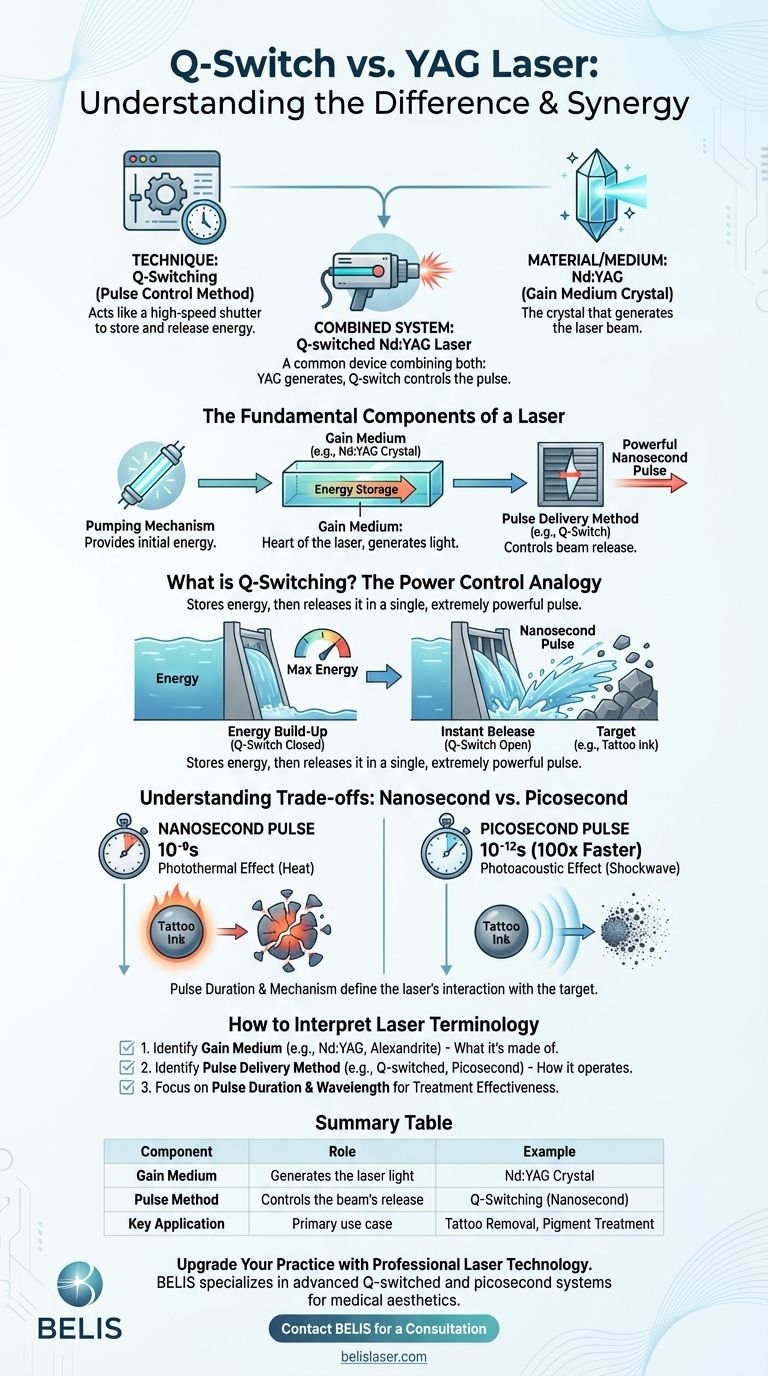
To be precise, the question isn't about Q-switch versus YAG, but rather how they work together. The core of the confusion lies in comparing a technique to a material. "YAG" (specifically Nd:YAG) is the crystal medium that generates a laser beam, while "Q-switching" is a method used to control that beam, forcing it into extremely short and powerful pulses. Therefore, a very common and effective device is the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser, which combines both of these elements.
The central confusion arises from treating a technique (Q-switching) and a laser medium (YAG) as separate, competing technologies. In reality, Q-switching is a method used to make a YAG laser produce high-energy pulses, creating a powerful tool for applications like tattoo removal.
The Fundamental Components of a Laser
To understand the relationship, you must first understand that a laser is a system with several key parts. Thinking of them as separate components clarifies their individual roles.
The Gain Medium: The Heart of the Laser (e.g., YAG)
The gain medium is the material that, when stimulated by energy, generates the laser light. This medium can be a gas (like CO2), a liquid, or a solid-state crystal.
Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) is a very common and versatile solid-state crystal used as a gain medium. It is the "engine" of the laser.
The Pumping Mechanism: The Energy Source
The gain medium must be "pumped" with energy to excite its atoms. This is typically done with a flashlamp or another laser, providing the initial power that will be converted into a laser beam.
The Pulse Delivery Method: The "Shutter" (e.g., Q-Switch)
Left on its own, a continuously pumped laser would emit a steady, continuous beam. For many applications, what's needed is a brief, intense burst of power. This is where pulse control methods like Q-switching come in.
What is Q-Switching? The Power Control System
Q-switching is a technique that acts like a high-speed optical shutter inside the laser cavity. It allows the gain medium (the YAG crystal) to store up a massive amount of energy before releasing it all at once.
How It Works: Building and Releasing Energy
Imagine a dam holding back a river. The Q-switch "dams" the light, preventing the laser from firing while the YAG crystal absorbs more and more energy from the pump source.
When the energy in the crystal is at its absolute peak, the Q-switch "opens the dam" instantly. This releases all the stored energy in a single, extremely powerful and brief pulse of light.
The Result: Nanosecond Pulses
This process creates pulses with a duration in the nanosecond range (one billionth of a second). These pulses have an exceptionally high peak power, making them ideal for shattering small targets like tattoo ink particles or skin pigment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Nanosecond vs. Picosecond
Your reference mentions PicoSure, which introduces the next evolution in pulse technology: picosecond lasers. This is where the pulse duration, not the laser medium itself, becomes the critical point of comparison.
Pulse Duration: The Key Differentiator
A Q-switched laser operates in the nanosecond (one billionth of a second) range. A picosecond laser, as its name implies, operates in the picosecond (one trillionth of a second) range—a pulse roughly 100 times shorter.
Mechanism of Action: Photothermal vs. Photoacoustic
This difference in speed changes how the laser interacts with its target.
Q-switched (nanosecond) lasers primarily work through a photothermal effect. They deliver energy that rapidly heats the target (like a tattoo ink particle), causing it to shatter from thermal expansion.
Picosecond lasers operate so quickly that heat has little time to build up. They work through a photoacoustic effect, creating a powerful shockwave that pulverizes the target into much finer dust-like particles with less heat transfer to surrounding tissue.
Clarifying the Technology
It is also important to note that while many Q-switched lasers use an Nd:YAG crystal, not all picosecond lasers do. For instance, the original PicoSure device uses an Alexandrite crystal, not YAG. This highlights that the pulse duration (pico vs. nano) and the gain medium (YAG vs. Alexandrite) are separate specifications.
How to Interpret Laser Terminology
When evaluating a laser system for a specific application, you must look at its components to understand its capabilities.
- If your primary focus is to understand a specific device: Identify its gain medium (e.g., Nd:YAG, Alexandrite) and its pulse delivery method (e.g., Q-switched, picosecond, continuous wave).
- If your primary focus is to choose a treatment: Focus on the pulse duration (nanosecond vs. picosecond) and the wavelength, as these factors determine effectiveness and safety for your specific need, like tattoo color or skin type.
- If your primary focus is to avoid confusion: Remember that a "Q-switched Nd:YAG laser" is a single device where "Q-switched" describes how it operates and "Nd:YAG" describes what it's made of.
Understanding these core principles allows you to move beyond marketing terms and evaluate laser technologies based on their fundamental capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Gain Medium | Generates the laser light | Nd:YAG Crystal |
| Pulse Method | Controls the beam's release | Q-Switching (Nanosecond) |
| Key Application | Primary use case | Tattoo Removal, Pigment Treatment |
Upgrade Your Practice with Professional Laser Technology
BELIS specializes in advanced medical aesthetic equipment, including Q-switched and picosecond laser systems. We help medical aesthetics clinics and premium beauty salons enhance treatment outcomes, improve client satisfaction, and grow their business with reliable, high-performance technology.
Contact BELIS today for a personalized consultation to find the perfect laser solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Clinic Use IPL and SHR Hair Removal Machine with Nd Yag Laser Tattoo Removal
- Pico Picosecond Laser Machine for Tattoo Removal Picosure Pico Laser
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Clinic Diode Laser Hair Removal Machine with SHR and Trilaser Technology
- Diode Tri Laser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
People Also Ask
- Does IPL work on all hair types? The Truth About Melanin & Hair Removal Success
- Can you use a hair removal device on private parts? A Safe Zone Guide for Intimate Areas
- What are the negative effects of IPL? Understanding Risks for Safe Treatment
- Can I use my IPL machine every week? A Guide to the Optimal At-Home Treatment Schedule
- Why is SPF 50 mandatory after IPL for vascular lesions? Protect Your Skin and Ensure Flawless Results