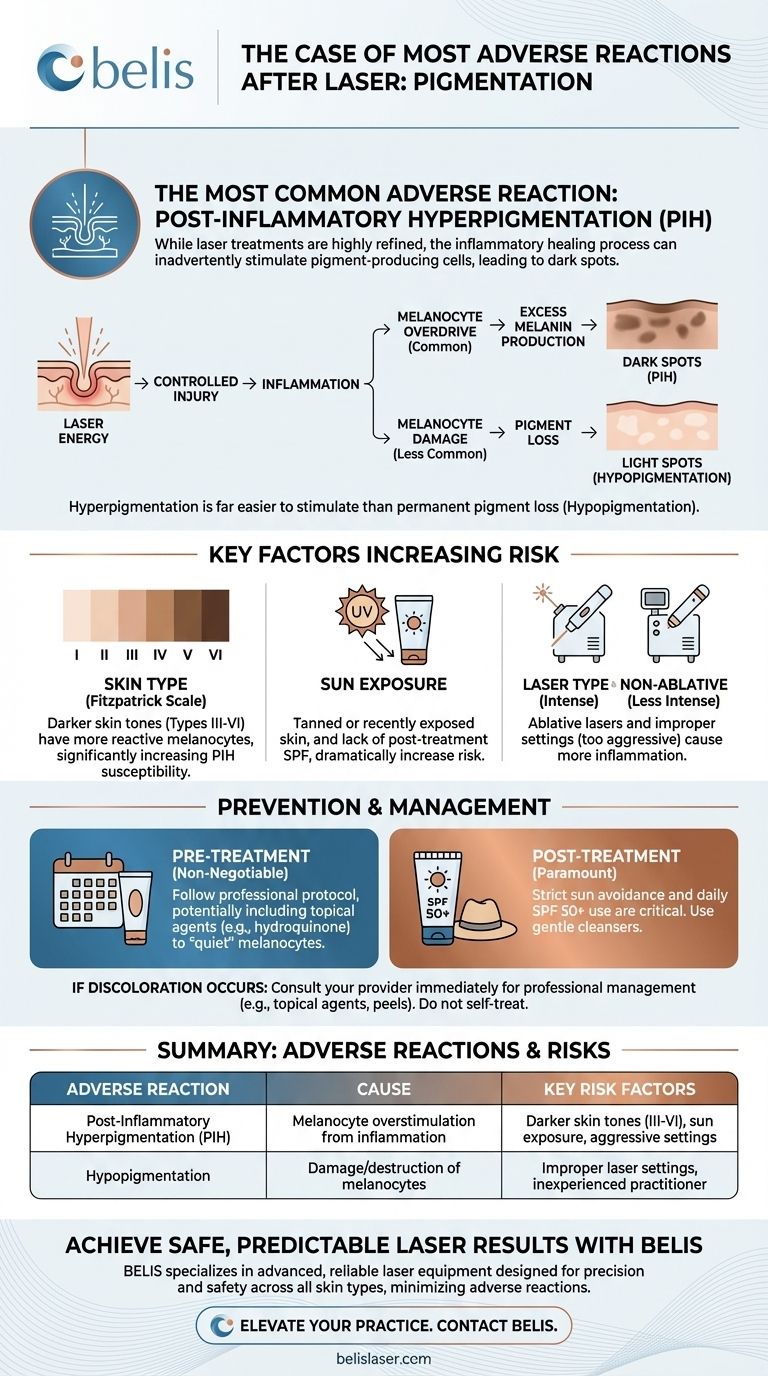
The most common adverse reaction following laser skin treatments is a change in skin pigmentation. Specifically, the development of dark spots, known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), is the most frequently reported complication, occurring more often than the lightening of skin (hypopigmentation).
While modern laser procedures are highly refined, the skin's response to the controlled injury they create is not always predictable. The core issue is the inflammatory healing process, which can inadvertently stimulate your pigment-producing cells, leading to discoloration that wasn't there before.
Understanding Post-Laser Pigmentation
Laser treatments work by delivering focused energy into the skin to achieve a specific goal, like removing hair, resurfacing wrinkles, or breaking up unwanted pigment. This energy intentionally creates a controlled injury, which triggers a healing response. The most common side effect relates to how your pigment cells (melanocytes) react to this healing process.
What is Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)?
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is the technical term for the dark spots that can appear after the skin has been inflamed or injured.
The laser's energy creates inflammation. In response, your melanocytes can go into overdrive, producing excess melanin and depositing it in the skin. This results in flat spots of discoloration that can appear pink, red, brown, or black, depending on your skin tone.
What is Hypopigmentation?
Hypopigmentation is the opposite and less common outcome. It is the loss of skin color, resulting in patches that are lighter than your surrounding skin.
This occurs if the laser energy is too aggressive or improperly administered, causing thermal damage that stuns or destroys the melanocytes. When these cells can no longer produce melanin effectively, the skin loses its pigment in that area.
Why Hyperpigmentation is More Common
The body's natural healing cascade involves inflammation, which is a direct signal for melanocytes to become active. It is far easier to stimulate an overproduction of melanin (PIH) than it is to cause the level of permanent damage required to destroy melanocytes and cause a loss of pigment (hypopigmentation).
Key Factors That Increase Risk
Not everyone has the same risk of developing pigmentation issues. The probability is heavily influenced by your genetics, your behavior, and the skill of your practitioner.
The Critical Role of Skin Type
The single most important predictor is your skin tone, often classified on the Fitzpatrick scale.
Individuals with darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick types III-VI) naturally have more active and reactive melanocytes. This makes them significantly more susceptible to developing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation after any skin trauma, including a laser treatment.
Sun Exposure Before and After
Sun exposure is a direct command for your melanocytes to produce pigment.
Treating skin that is tanned or recently sun-exposed dramatically increases the risk of an unpredictable pigment response. Likewise, failing to protect the skin from the sun with a high-SPF, broad-spectrum sunscreen after treatment is a primary cause of PIH.
The Type and Intensity of the Laser
Different lasers carry different risk profiles. Ablative lasers (like CO2 or Erbium), which remove the outer layer of skin, create a more intense inflammatory response and carry a higher risk of PIH than non-ablative lasers, which heat the underlying tissue without disrupting the surface.
Furthermore, an inexperienced operator using incorrect settings—too much energy or an improper wavelength for your skin type—can easily cause the excess inflammation that leads to discoloration.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Prevention and Management
While pigmentation changes are a known risk, they are often preventable and manageable. The trade-off for a successful outcome is strict adherence to professional guidance before and after your procedure.
Pre-Treatment Preparation is Non-Negotiable
Your practitioner may prescribe a pre-treatment protocol, especially for higher-risk skin tones. This can include using topical agents like hydroquinone or retinoids for several weeks to "quiet down" the melanocytes and make them less reactive to the upcoming laser treatment.
Post-Treatment Care is Paramount
Following your procedure, diligent aftercare is your primary defense. This means strict sun avoidance and the daily application of a broad-spectrum SPF 50+ sunscreen, even on cloudy days. Using gentle cleansers and avoiding any harsh scrubs or exfoliants is also crucial to let the skin heal without additional irritation.
If Discoloration Occurs
If PIH does develop, it is important not to panic. In many cases, it is temporary and will fade over several months with diligent sun protection. Your provider can also recommend treatments like topical lightening agents, chemical peels, or additional light-based therapies to speed up resolution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the potential for pigmentation changes allows you to take control of the process and minimize your risk.
- If your primary focus is safety: Choose a board-certified dermatologist or plastic surgeon with extensive experience performing laser treatments on your specific skin type.
- If you have a darker skin tone (Fitzpatrick III+): Your highest priority is preventing PIH. This means strictly following all pre- and post-care instructions, especially regarding sun avoidance and any prescribed topical creams.
- If you have already developed discoloration: Do not attempt to self-treat with aggressive products. Consult your provider immediately for a professional management plan to avoid making the issue worse.
Ultimately, knowing the risks and how to mitigate them is the most critical step toward achieving a safe and successful laser treatment outcome.
Summary Table:
| Adverse Reaction | Cause | Key Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH) | Melanocyte overstimulation from inflammation | Darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick III-VI), sun exposure, aggressive laser settings |
| Hypopigmentation | Damage/destruction of melanocytes | Improper laser settings, inexperienced practitioner |
Achieve Safe, Predictable Laser Results with BELIS
Pigmentation issues are a primary concern for any clinic offering laser treatments. At BELIS, we specialize in providing medical aesthetic clinics and premium beauty salons with advanced, reliable laser equipment designed for precision and safety across all skin types.
Our professional-grade devices feature intelligent technology to help minimize adverse reactions, empowering you to deliver exceptional results with confidence. Let us help you enhance your service offerings and build client trust.
Contact BELIS today for a consultation on our professional medical aesthetic equipment and elevate your practice's standards.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Pico Picosecond Laser Machine for Tattoo Removal Picosure Pico Laser
- Pico Laser Tattoo Removal Machine Picosure Picosecond Laser Machine
- Multifunctional Laser Hair Growth Machine Device for Hair Growth
- Multifunctional Laser Hair Growth Machine Device for Hair Growth
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of Pico laser machines? Achieve Faster Results and Safer Skin Rejuvenation
- Why are high-precision laser parameters used in LADD? Optimize Drug Delivery and Safety with Precision Control
- What is the longevity of Pico laser treatment results? Maximize Your Skin Transformation and Durability
- For which applications are Pico lasers considered versatile? A Guide to Elite Skin Restoration
- What are the benefits of picosecond machines? Comparing Picosecond vs Nanosecond Lasers for Tattoo Removal



















