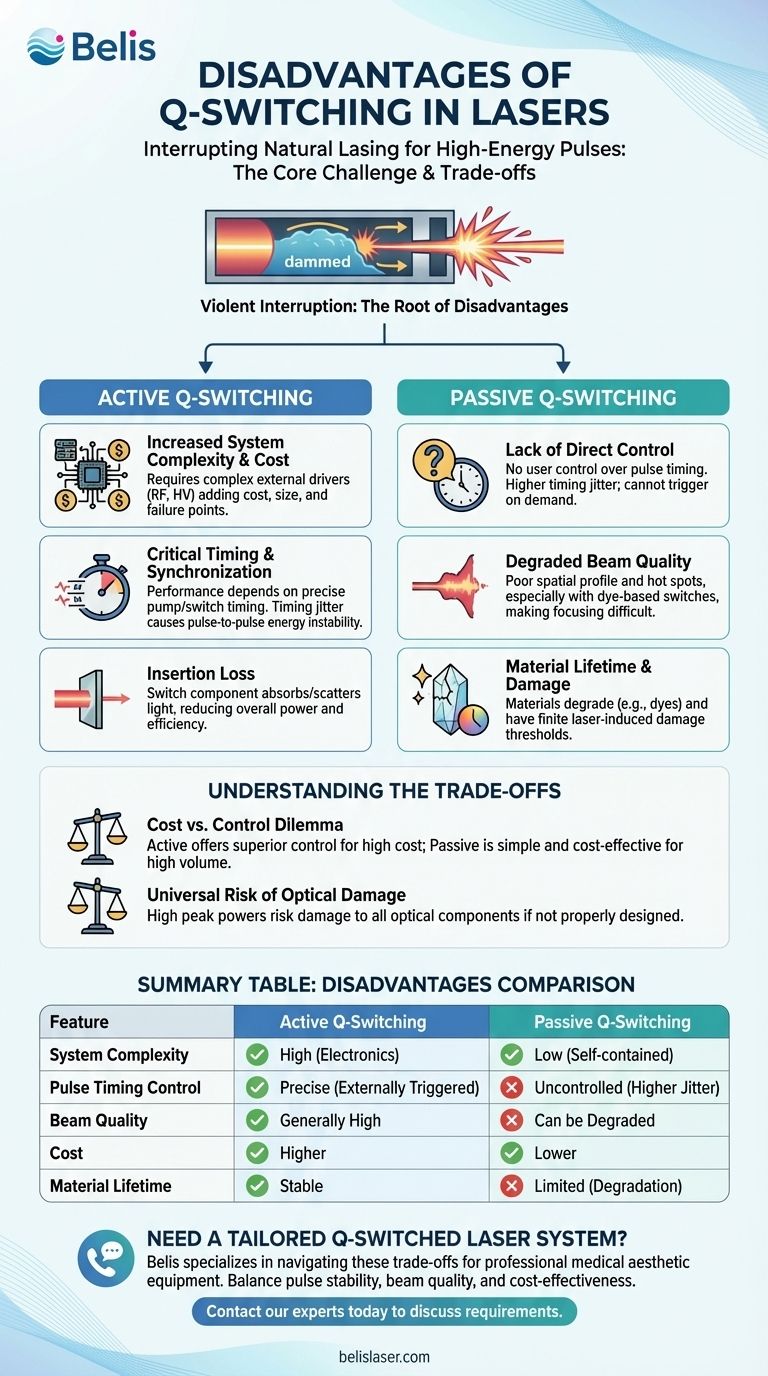
While Q-switching is the go-to technique for generating high-energy, nanosecond laser pulses, it is not without significant drawbacks. The disadvantages are not uniform across all systems; they depend heavily on the specific Q-switching method employed, introducing trade-offs between system complexity, cost, pulse stability, and the quality of the laser beam itself.
Q-switching forces a laser to operate in an extreme, pulsed regime far from its natural state. Consequently, its disadvantages are not flaws in the concept but practical consequences of the method used: active methods introduce complexity and cost, while passive methods can sacrifice control and beam quality.
The Core Challenge: Interrupting Natural Lasing
A laser's gain medium naturally wants to release energy as soon as it reaches the threshold for lasing. Q-switching works by deliberately preventing this, effectively "damming" the energy within the laser cavity to build it to a much higher level before releasing it all at once.
This violent interruption of the natural process is the root source of the associated disadvantages. The specific drawbacks emerge from the device used to create this temporary blockage—the Q-switch.
Disadvantages of Active Q-Switching
Active Q-switches use an external power source to control the cavity loss, typically with an Acousto-Optic (AO) or Electro-Optic (EO) modulator. This provides excellent control but comes with its own set of problems.
Increased System Complexity and Cost
Active modulators are complex components that require dedicated external electronics. These include high-frequency RF drivers (for AO switches) or high-voltage power supplies (for EO switches), adding significant cost, size, and potential points of failure to the laser system.
Critical Timing and Synchronization
The performance of an actively Q-switched laser depends on precise timing between the pump source and the opening of the Q-switch. Any electronic delay or timing jitter in the control signal translates directly into pulse-to-pulse energy instability, which is unacceptable for many precision applications.
Insertion Loss
Placing any component inside the laser cavity introduces some level of insertion loss, meaning the component itself absorbs or scatters a small fraction of the laser light. This slightly reduces the laser's overall power and efficiency.
Disadvantages of Passive Q-Switching
Passive Q-switches, such as a saturable absorber crystal (like Cr:YAG) or a dye cell, work automatically without external electronics. They switch from opaque to transparent when the light intensity inside the cavity reaches a certain threshold. This simplicity is their main advantage, but it creates other limitations.
Lack of Direct Control
With a passive Q-switch, the user has no direct control over the pulse timing. The laser will fire whenever enough energy has been stored, leading to higher timing jitter compared to active systems. You cannot trigger a pulse on demand.
Degraded Beam Quality
Some passive methods are notorious for producing poor-quality beams. As noted in research, a dye Q-switch often "opens" unevenly as the dye material bleaches. This non-uniform switching imparts a poor spatial profile onto the laser beam, creating hot spots and making it difficult to focus.
Material Lifetime and Damage
The materials in passive Q-switches can degrade. Organic dyes have a limited lifetime and must be replaced. Solid-state saturable absorbers have a finite laser-induced damage threshold and can be permanently damaged by the very high optical power they are designed to manage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of Q-switching method is a decision based on balancing competing priorities.
The Cost vs. Control Dilemma
Active Q-switching offers superior control over pulse energy, timing, and repetition rate, making it ideal for scientific and advanced industrial applications. This control comes at a higher cost and complexity.
Passive Q-switching is far simpler, more compact, and more cost-effective. It is the clear choice for high-volume, low-cost applications where precise timing is not the primary concern.
The Universal Risk of Optical Damage
Regardless of the method, all Q-switched lasers produce extremely high peak powers. This creates an ever-present risk of damaging the laser's own optical components—mirrors, crystals, and the Q-switch itself—if the system is not designed with sufficient damage-resistance margins.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the "disadvantages" of a Q-switching method are only disadvantages if they conflict with your application's requirements.
- If your primary focus is precise external triggering and high pulse-to-pulse stability (e.g., advanced materials processing, LIDAR): An active Q-switch is necessary, and you must budget for its cost and complexity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and simplicity for a mass-produced device (e.g., handheld laser markers, tattoo removal): A passive Cr:YAG Q-switch is the superior choice, as its timing jitter is acceptable for these tasks.
- If your application is highly sensitive to a clean, uniform beam profile (e.g., fine micromachining, medical ophthalmology): You must carefully vet the Q-switch, as passive dye-based systems are often unsuitable and even some crystal-based systems can introduce beam distortion.
Understanding these inherent limitations allows you to select a Q-switched system not just for its peak power, but for its fundamental alignment with your specific operational needs.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Active Q-Switching | Passive Q-Switching |
|---|---|---|
| System Complexity | High (external electronics) | Low (self-contained) |
| Pulse Timing Control | Precise, externally triggered | Uncontrolled, higher jitter |
| Beam Quality | Generally high | Can be degraded (e.g., dye-based) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Material Lifetime | Stable | Limited (e.g., dye degradation) |
Need a Q-switched laser system tailored to your specific application?
BELIS specializes in professional medical aesthetic equipment, serving medical aesthetics clinics and premium beauty salons. We help you navigate the trade-offs between active and passive Q-switching to deliver optimal performance for procedures like tattoo removal or precision skin treatments.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions balance pulse stability, beam quality, and cost-effectiveness for your business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Q Switch Nd Yag Laser Machine Tattoo Removal Nd Yag Machine
- 7D 12D 4D HIFU Machine Device
- Fractional CO2 Laser Machine for Skin Treatment
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Multifunctional Laser Hair Growth Machine Device for Hair Growth
People Also Ask
- How many treatment sessions are typically required with the Q-Switched Nd:YAG laser? A Guide to Professional Results
- How does a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser remove tattoos and permanent make-up? Achieve Safe and Effective Pigment Clearance
- What types of skin disorders can be treated with a neodymium YAG laser? Comprehensive Guide to Laser Skin Solutions
- How does a Q-switched Nd: YAG laser technically function during treatment? Advanced Pulse Physics Explained
- What is the lasing medium in an Nd:YAG laser? Unlock the Power of Neodymium-Doped YAG Crystals



















