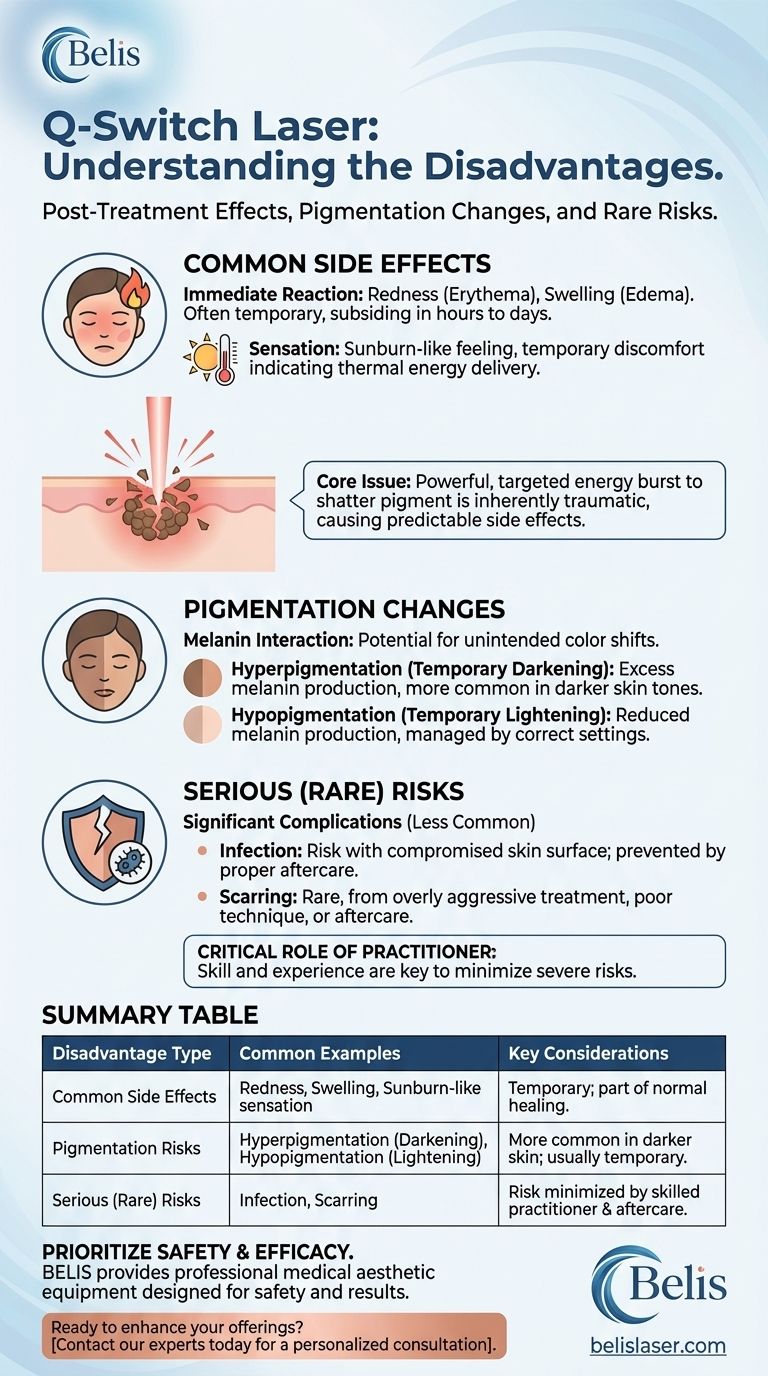
The primary disadvantages of a Q-switch laser are the expected post-treatment side effects, such as redness, swelling, and a sensation similar to sunburn. More significant risks, though less common, include temporary changes in skin pigmentation (darkening or lightening) and, in rare instances, the potential for infection or scarring.
The core issue is that a Q-switch laser works by delivering a powerful, targeted burst of energy to shatter pigment. This process, while effective, is inherently traumatic to the skin, leading to a predictable set of side effects and potential risks that must be carefully managed.

Immediate and Common Side Effects
The most common disadvantages are temporary and a direct result of the skin's natural healing response to the laser's intense energy.
Redness and Swelling
Immediately following the procedure, it is normal to experience redness (erythema) and swelling (edema) in the treated area. This is a standard inflammatory response and typically subsides within a few hours to a couple of days.
A Sunburn-like Sensation
Patients often describe the feeling as similar to a mild sunburn. This discomfort is temporary and is a sign that the laser has successfully delivered thermal energy into the skin.
Potential Pigmentation Changes
The laser's interaction with the skin's melanin can sometimes lead to unintended changes in skin color, which are usually temporary.
Hyperpigmentation (Temporary Darkening)
The skin may respond to the laser's energy by producing excess melanin, causing the treated area to darken. This is known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) and is more common in individuals with darker skin tones.
Hypopigmentation (Temporary Lightening)
Conversely, the laser can sometimes temporarily reduce melanin production, leading to a lightening of the skin in the treated area. This risk is managed by using appropriate laser settings for the patient's skin type.
Understanding the More Serious (But Rarer) Risks
While Q-switch lasers are considered safe when operated by a qualified professional, more significant complications can occur.
Risk of Infection
Any procedure that compromises the skin's surface carries a risk of infection. Following post-treatment care instructions, such as keeping the area clean and protected, is critical to prevent this.
Potential for Scarring
Scarring is a rare but serious risk. It can result from an overly aggressive treatment, improper technique by the practitioner, or poor aftercare by the patient (such as picking at scabs or blisters).
The Critical Role of the Practitioner
Many of the most severe disadvantages are tied directly to the skill and experience of the person operating the laser. An unqualified technician can easily use the wrong settings, increasing the likelihood of burns, scarring, and permanent pigment changes.
How to Minimize Risks and Make an Informed Decision
Understanding your goals and choosing the right provider are the most important steps you can take to mitigate the disadvantages of Q-switch laser treatment.
- If your primary focus is safety: Choose a board-certified dermatologist or a highly experienced, licensed practitioner who specializes in laser treatments for your specific skin type.
- If you have a darker skin tone: You must seek a provider with extensive experience treating skin of color to minimize the significant risk of hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
- If you are highly risk-averse: Ensure you have a thorough consultation to discuss all potential side effects and confirm that the expected outcome is worth the temporary discomfort and recovery time.
Ultimately, a successful outcome depends on a skilled practitioner correctly assessing your skin and a diligent patient committed to proper aftercare.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Type | Common Examples | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Common Side Effects | Redness, swelling, sunburn-like sensation | Temporary; part of the normal healing process. |
| Pigmentation Risks | Hyperpigmentation (darkening), Hypopigmentation (lightening) | More common in darker skin tones; usually temporary. |
| Serious (Rare) Risks | Infection, Scarring | Risk is minimized by a skilled practitioner and proper aftercare. |
Prioritize Safety and Efficacy with Professional Equipment
Understanding the potential side effects of Q-switch laser treatment is the first step toward a safe and successful outcome. The second, and most critical, step is ensuring your clinic is equipped with reliable, advanced technology and that your practitioners are fully trained.
BELIS specializes in providing professional medical aesthetic equipment to clinics and premium beauty salons. Our advanced laser systems are designed with safety features to help mitigate risks, supporting your team in delivering exceptional results for your clients.
Ready to enhance your treatment offerings with confidence? Let's discuss how our technology can fit your practice's needs.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Q Switch Nd Yag Laser Machine Tattoo Removal Nd Yag Machine
- Clinic Use IPL and SHR Hair Removal Machine with Nd Yag Laser Tattoo Removal
- Pico Picosecond Laser Machine for Tattoo Removal Picosure Pico Laser
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Clinic Diode Laser Hair Removal Machine with SHR and Trilaser Technology
People Also Ask
- How does the 1064nm Nd:YAG laser treat deep hypertrophic scar tissue? Unlock Advanced Dermal Remodeling Solutions
- What are the technical considerations for utilizing a 40 ms pulse width? Optimize Long-pulsed Nd:YAG Laser Safety
- What advantage does a 7mm spot size provide for Melasma treatment? Maximize Depth and Safety with Nd:YAG Lasers
- How does the Nd:YAG laser work? Unlocking Deep-Tissue Precision for Medical Aesthetics
- What are the advantages of using Nd:YAG lasers? Discover Versatility for Safe Skin Care & Precision



















