While highly effective for many, diode laser hair removal is not without its potential downsides. The primary disadvantages include limited effectiveness on very light or fine hair, the risk of temporary skin inflammation like folliculitis, and the potential for burns or redness, which is almost always tied to improper application of the technology.
The most significant risks associated with diode laser hair removal are not inherent flaws in the technology itself, but rather outcomes directly related to its proper use. The treatment's success and safety are critically dependent on the hair/skin type match and the skill of the operator.
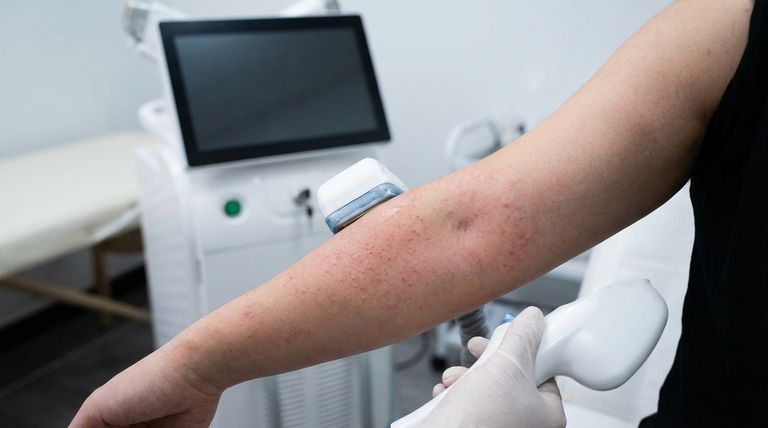
The Core Limitations of the Technology
To understand the cons, you must first understand how the laser works. A diode laser emits a specific wavelength of light that is absorbed by melanin—the pigment that gives hair its dark color.
The Challenge with Light and Fine Hair
The laser's energy requires a dark, pigmented target to be effective. This creates a significant limitation for certain hair types.
Very light-colored hair, such as blonde, red, or gray, contains very little melanin. Without a sufficient target, the laser energy is not absorbed by the hair follicle and the treatment is rendered ineffective.
Potential Side Effects and Skin Reactions
Even when performed correctly, the introduction of concentrated light energy into the skin can cause temporary reactions as the body responds to the treatment.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, which can appear as small, red bumps in the treated area.
This occurs as the laser energy damages the follicles, prompting a temporary inflammatory response from the body. It typically resolves on its own within a few days.
Temporary Redness and Swelling
It is very common to experience some redness and mild swelling immediately following a session. This is a normal, expected reaction to the heat produced by the laser and is a sign that the follicles have responded to the treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Operator Skill vs. Technology Risk
The most serious potential cons are not guaranteed side effects but risks that emerge from improper use. The distinction is critical.
The Risk of Burns and Pigmentation Changes
A burn is not a normal side effect; it is an indication of operator error. This happens when the laser's energy setting is too high for the patient's specific skin type.
Instead of being selectively absorbed by the hair follicle, the excess energy is absorbed by the surrounding skin, causing damage. This can lead to burns, blisters, or changes in skin pigmentation (hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation).
The Critical Role of the Technician
Nearly all severe adverse effects can be traced back to a lack of proper assessment or skill. A qualified and experienced technician will perform a patch test and correctly classify your skin type to select a safe and effective energy setting.
Choosing a reputable provider is the single most important factor in mitigating the risks associated with diode laser treatments.
How to Minimize Your Risk
Your approach to diode laser hair removal should be guided by your specific profile and a clear understanding of the risks.
- If you have light blonde, red, or gray hair: You should seriously consider that diode lasers will be ineffective and explore alternative long-term hair removal methods.
- If you have the appropriate dark hair and lighter skin type: Your primary focus must be on vetting the clinic and ensuring the technician is certified and experienced to prevent burns and other adverse effects.
- If you are concerned about temporary reactions: Discuss post-treatment care with your provider to manage expected redness and folliculitis, ensuring a smoother recovery.
Ultimately, a well-informed patient who chooses a highly skilled provider is in the best position to achieve excellent results safely.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Limitation/Risk | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Hair Type | Ineffective on light blonde, red, or gray hair | Requires sufficient melanin (dark pigment) to work |
| Common Side Effects | Temporary redness, swelling, folliculitis | Normal inflammatory response; usually resolves quickly |
| Serious Risks | Burns, blisters, pigmentation changes | Almost always a result of operator error, not the technology itself |
| Key Factor | Operator skill and experience | The single most important factor for safety and effectiveness |
Achieve Safe and Effective Hair Removal with BELIS
Understanding the technology is the first step; choosing the right partner is the next. The risks associated with diode laser hair removal are significantly minimized when using professional-grade equipment operated by trained experts.
BELIS specializes in providing professional medical aesthetic equipment to clinics and premium beauty salons. Our advanced diode laser systems are engineered for precision and safety, empowering your technicians to deliver superior results for clients with the appropriate hair and skin types.
Ready to enhance your service offerings and client safety? Let our experts help you select the ideal technology for your practice.
Contact BELIS today for a professional consultation
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Diode Tri Laser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Trilaser Diode Hair Removal Machine for Beauty Clinic Use
- Clinic Diode Laser Hair Removal Machine with SHR and Trilaser Technology
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Clinic Use IPL and SHR Hair Removal Machine with Nd Yag Laser Tattoo Removal
People Also Ask
- In what way do energy density and spot size work together for laser hair removal? Unlock Superior Clinical Efficacy
- How do professional-grade laser systems function? A Deep Dive into Selective Photothermolysis for Clinics
- What are the technical advantages of Pulse Burst technology vs. long-pulse in laser hair removal? Master Safety & Power
- What is the clinical significance of performing slit lamp and fundus examinations? Key Ocular Safety Post-Laser
- In what scenarios is Static Mode applied during laser hair removal? Master Precision for Stubborn Hair



















