At its core, a laser tattoo removal machine shatters ink particles embedded in your skin using an intensely focused beam of light. These rapid pulses of light energy are absorbed by the tattoo ink, causing the large particles to break apart into microscopic fragments. Your body's immune system then naturally clears away these tiny fragments over the following weeks, causing the tattoo to fade.
The laser itself does not remove the ink from your body. Instead, it acts as a tool to break the ink into pieces small enough for your body's natural "cleanup crew"—the immune system—to identify and dispose of.
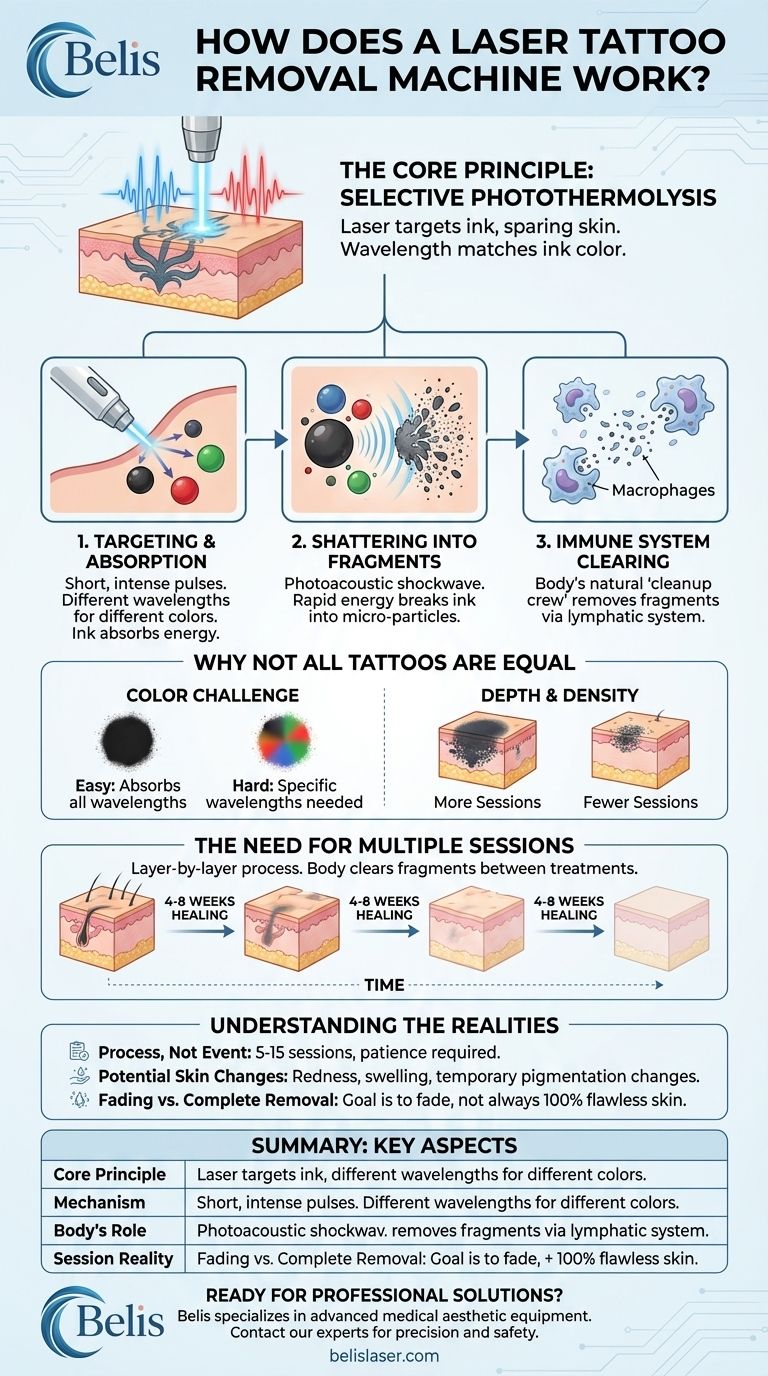
The Core Principle: Selective Photothermolysis
The science behind laser tattoo removal is a principle called selective photothermolysis. This sounds complex, but it breaks down into three simple concepts that ensure the laser targets the ink while protecting the surrounding skin.
### Targeting the Ink, Sparing the Skin
Each color of tattoo ink acts as a "target," known as a chromophore, that absorbs a specific wavelength (color) of light. The laser is calibrated to emit a wavelength that is strongly absorbed by the ink but poorly absorbed by the surrounding skin tissue.
This selective absorption means the laser's energy is concentrated almost exclusively on the ink, minimizing damage to the skin around it.
### From Solid Ink to Micro-Particles
A tattoo removal laser delivers its energy in incredibly short but powerful pulses, lasting only nanoseconds or even picoseconds (trillionths of a second). This rapid energy delivery creates a photoacoustic shockwave.
Instead of slowly burning the ink, this shockwave effect acts like a hammer, instantly shattering the large, solid ink particles into a fine dust. Imagine breaking a large rock into tiny pebbles—the material is the same, but the form is drastically different.
### The Role of Your Immune System
Your body cannot remove the original tattoo ink because the particles are too large for your immune cells to engulf. However, once the laser has shattered them into microscopic fragments, this changes.
Scavenger cells in your body, called macrophages, can now identify and "eat" these tiny ink particles. They are then transported through the lymphatic system and processed out of the body, just like any other foreign waste product. This clearing process is gradual and is why a tattoo continues to fade for weeks after a laser session.
Why Not All Tattoos Are Equal
The effectiveness and duration of the removal process depend heavily on the tattoo itself. Several factors determine why some tattoos fade in a few sessions while others require a dozen or more.
### The Challenge of Color
Black ink is the easiest to remove because it absorbs all laser wavelengths. It's a universal target.
Colored inks are more challenging. Colors like red, orange, and warm tones respond well to certain laser wavelengths (like 532nm). However, blues, greens, and purples require different, more specialized laser wavelengths (like 694nm or 755nm) that not all clinics possess.
### Ink Depth and Density
A professional tattoo artist typically injects ink deeply and uniformly into the dermis layer of the skin. This dense concentration of ink requires more sessions to break down layer by layer.
Amateur or older tattoos are often applied with less ink and at shallower depths, making them easier and faster to remove.
### The Need for Multiple Sessions
A single laser treatment can only safely shatter the topmost layer of ink particles. After the session, your body needs 4 to 8 weeks to clear away the shattered fragments and heal.
Once that layer is gone, the next session can target the layer of ink that was previously underneath. This layered approach is why multiple treatments spaced several weeks apart are non-negotiable for successful removal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Realities
While highly effective, laser tattoo removal is a significant commitment. Understanding the realities of the process is crucial for managing expectations.
### It's a Process, Not an Event
Complete removal is a marathon, not a sprint. The average professional tattoo requires anywhere from 5 to 15 sessions. Patience is essential, as the results appear gradually over many months or even years.
### Potential for Skin Changes
The process is safe when performed by a qualified technician, but side effects can occur. Short-term effects include redness, swelling, blistering, and scabbing, which are part of the normal healing process.
More lasting risks include hypopigmentation (lightening of the natural skin tone) or hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin). These risks are higher with improper aftercare or an inexperienced operator.
### Fading vs. Complete Removal
The goal of laser removal is to fade a tattoo to the point where it is no longer noticeable. While many tattoos can be completely cleared, 100% removal back to flawless skin is not always possible, especially with stubborn colors like turquoise or yellow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the mechanism of laser removal allows you to set realistic goals for your specific situation.
- If your primary focus is removing an old, black ink tattoo: You have the most straightforward case, which will likely require the fewest sessions and be highly effective.
- If your primary focus is removing a new, multi-colored tattoo: Be prepared for a longer, more complex, and potentially more expensive process that requires a clinic with multiple laser wavelengths.
- If your primary focus is lightening a tattoo for a cover-up: You may only need 2 to 4 sessions to fade the old design enough for a tattoo artist to create a new piece over it.
By understanding that the laser is just the first step, you can approach the tattoo removal process as an informed partner in your body's own healing and clearing capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | How It Works |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Selective Photothermolysis targets ink particles while sparing surrounding skin. |
| Mechanism | Short, powerful laser pulses create a shockwave that shatters ink into microscopic fragments. |
| Body's Role | The immune system's macrophages then naturally clear away the fragmented ink over several weeks. |
| Session Reality | Multiple sessions (typically 5-15) are needed, spaced 4-8 weeks apart for the body to heal and clear ink layers. |
Ready to offer safe, effective, and professional tattoo removal services?
BELIS specializes in professional medical aesthetic equipment, including advanced laser tattoo removal machines. Our devices are engineered for precision, safety, and superior results, helping medical aesthetics clinics and premium beauty salons expand their service offerings and enhance client satisfaction.
Contact our experts today to discover the right laser solution for your practice and learn how we can support your business growth.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Q Switch Nd Yag Laser Machine Tattoo Removal Nd Yag Machine
- Pico Laser Tattoo Removal Machine Picosure Picosecond Laser Machine
- Pico Picosecond Laser Machine for Tattoo Removal Picosure Pico Laser
- Clinic Use IPL and SHR Hair Removal Machine with Nd Yag Laser Tattoo Removal
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
People Also Ask
- How does the 1064nm Nd:YAG laser treat deep hypertrophic scar tissue? Unlock Advanced Dermal Remodeling Solutions
- How does the Nd:YAG laser work? Unlocking Deep-Tissue Precision for Medical Aesthetics
- What are Q-switched lasers commonly used for? Remove Tattoos & Pigment with Precision
- What are the technical considerations for utilizing a 40 ms pulse width? Optimize Long-pulsed Nd:YAG Laser Safety
- What are the advantages of using Nd:YAG lasers? Discover Versatility for Safe Skin Care & Precision



















