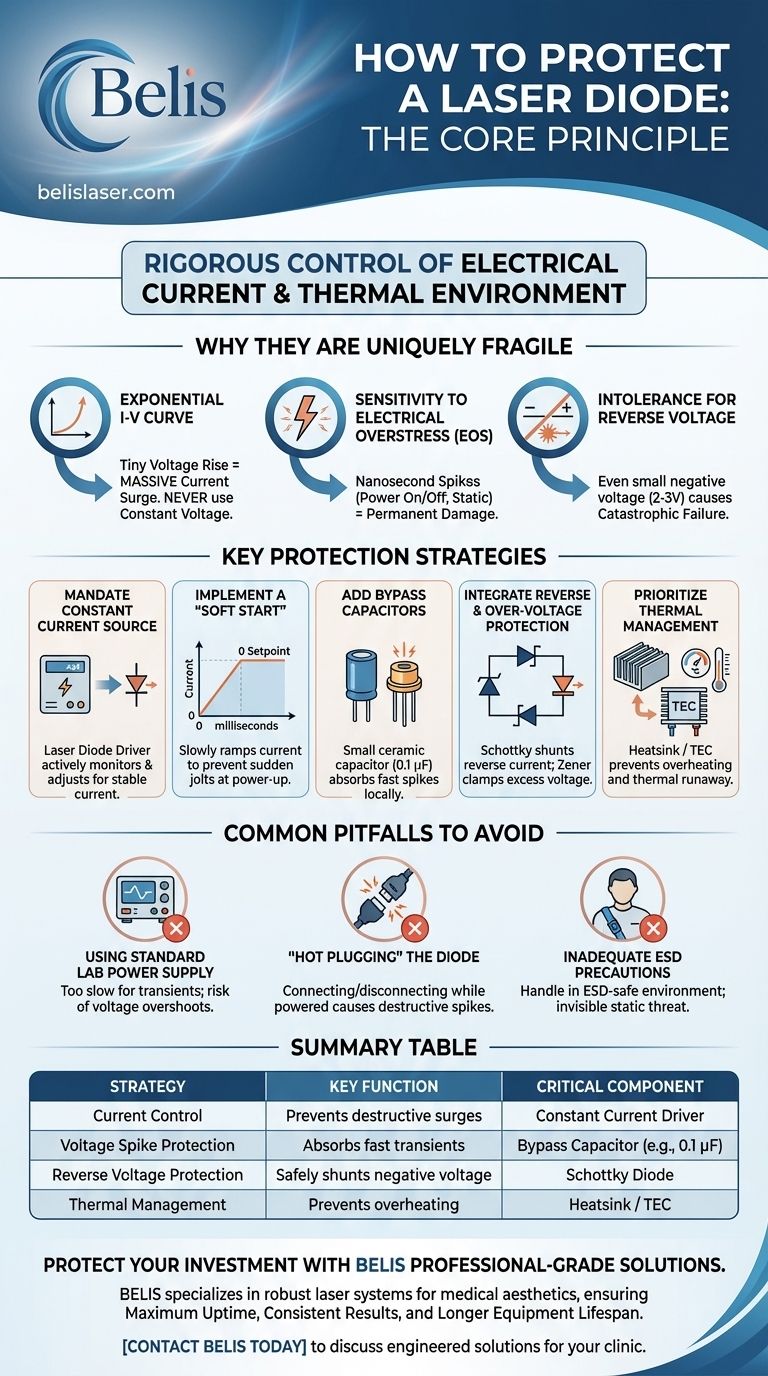
Protecting a laser diode boils down to one core principle: rigorously controlling the electrical current and thermal environment at all times. Because they are exceptionally sensitive to even momentary electrical spikes and reverse voltage, a standard power supply is inadequate and will likely destroy the component. Effective protection requires a multi-layered approach that addresses these vulnerabilities directly.
The fundamental mistake is treating a laser diode like an LED. A laser diode's optical output and lifespan are critically dependent on stable current and temperature. The only reliable protection is a dedicated laser diode driver that provides constant current, soft-start capabilities, and integrated safety features.

Why Laser Diodes Are Uniquely Fragile
To implement the correct protection, you must first understand the physics that make these components so sensitive. Their internal structure is fundamentally different from a simple resistor or even a standard LED.
The Exponential I-V Curve
A laser diode's current-voltage (I-V) relationship is exponential. This means a minuscule increase in voltage across the diode can cause a massive, potentially destructive surge in current.
This is why you never power a laser diode with a constant voltage source. A slight voltage drift or ripple, harmless to other components, can instantly push the current past its absolute maximum rating.
Sensitivity to Electrical Overstress (EOS)
Electrical Overstress (EOS) is damage caused by exposing a component to current or voltage beyond its specifications. For laser diodes, the most common form of EOS is a transient spike lasting mere nanoseconds.
These spikes can come from turning a power supply on or off, static discharge, or even noise from nearby equipment. This energy can permanently damage the delicate internal facets of the laser, causing an immediate drop in output power or total failure.
Intolerance for Reverse Voltage
Applying even a small negative voltage across a laser diode can cause immediate, catastrophic failure. Most laser diodes have a maximum reverse voltage rating of only 2-3 volts.
This is a common failure mode when power supplies are shut down improperly or when wiring mistakes are made.
Key Protection Strategies and Practices
Protecting your investment involves building a system that anticipates and neutralizes the threats mentioned above. These are not optional considerations; they are essential for reliable operation.
Mandate a Constant Current Source
This is the single most important rule. A dedicated laser diode driver operates as a constant current source. It actively monitors the current flowing through the diode and continuously adjusts its output voltage to maintain that current, regardless of temperature changes or other factors.
Implement a "Soft Start"
A soft-start circuit is critical for preventing the large current spike that can occur when power is first applied.
A proper driver will slowly ramp the current from zero to the setpoint over a few milliseconds, ensuring the diode is never subjected to a sudden jolt of energy.
Add Bypass Capacitors
A small ceramic capacitor (typically 0.1 µF) placed physically as close as possible to the laser diode's pins provides a crucial line of defense.
This capacitor acts as a local reservoir of charge, absorbing very fast voltage spikes and noise from the power lines before they can reach the diode itself.
Integrate Reverse and Over-Voltage Protection
A simple and effective method is to place a Schottky diode in parallel with the laser diode, but with reversed polarity.
If a negative voltage appears, the Schottky diode will turn on and safely shunt the current away from the laser. Zener diodes can also be used to clamp any voltage that exceeds the laser's forward voltage limit.
Prioritize Thermal Management
Heat is a silent killer of laser diodes. As a diode's temperature increases, its efficiency drops, and its required forward voltage for a given current decreases.
This can lead to thermal runaway in poorly controlled systems. A proper heatsink is mandatory. For high-power or high-stability applications, a Thermo-Electric Cooler (TEC) managed by the driver is essential to lock the diode's temperature.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Building trust in your system means understanding the common mistakes that lead to failure. Awareness is the first step in prevention.
Using a Standard Lab Power Supply
A benchtop power supply set to a "current limit" is not a true constant current source. Its response time is far too slow to protect the diode from fast transients during power-on, and its output can have significant voltage overshoots.
"Hot Plugging" the Laser Diode
Never connect or disconnect a laser diode while the driver circuit is powered on. This action is a primary source of destructive voltage and current spikes. Always power down the entire system before making any connection changes.
Inadequate ESD Precautions
Electrostatic Discharge is an invisible threat. Always handle laser diodes in an ESD-safe environment. This includes using a grounded wrist strap, working on an anti-static mat, and keeping the component in its anti-static packaging until the moment of installation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your protection strategy should match the demands of your application. The value of the diode and the cost of failure will dictate the level of investment required.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost experiment or hobby project: A dedicated integrated circuit (IC) laser driver with built-in soft-start and a properly sized heatsink is the absolute minimum requirement.
- If your primary focus is a high-power industrial or scientific application: A professional-grade benchtop or modular driver with integrated TEC control, multiple safety interlocks, and current ramping features is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is high-speed data communications: You need a specialized driver with extremely low-noise output and carefully selected bypass components that do not compromise the signal's bandwidth.
Ultimately, treating the protection circuitry as an integral and critical part of the laser system, not an afterthought, is the key to achieving reliability and success.
Summary Table:
| Protection Strategy | Key Function | Critical Component |
|---|---|---|
| Current Control | Prevents destructive current surges | Constant Current Laser Driver |
| Voltage Spike Protection | Absorbs fast transients | Bypass Capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF) |
| Reverse Voltage Protection | Safely shunts negative voltage | Schottky Diode |
| Thermal Management | Prevents overheating and thermal runaway | Heatsink / TEC (Thermo-Electric Cooler) |
Protect your investment in medical aesthetic technology with professional-grade laser diode solutions from BELIS.
Our expertise in designing and supplying robust laser systems ensures your clinic or premium beauty salon benefits from:
- Maximum Uptime: Reliable equipment protected against electrical and thermal stress.
- Consistent Results: Stable laser output for repeatable, high-quality treatments.
- Longer Equipment Lifespan: Proper protection extends the life of your critical devices.
BELIS specializes in professional medical aesthetic equipment, providing advanced laser diode drivers and integrated protection features tailored for demanding clinical environments.
Contact BELIS today to discuss how our engineered solutions can enhance the reliability and performance of your laser-based treatments.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Clinic Diode Laser Hair Removal Machine with SHR and Trilaser Technology
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Diode Tri Laser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
- Trilaser Diode Hair Removal Machine for Beauty Clinic Use
- Multifunctional Laser Hair Growth Machine Device for Hair Growth
People Also Ask
- Is diode laser better than IPL? Unlock Superior Hair Removal Results
- Can you use laser hair removal on intimate areas? Achieve Lasting Smoothness and Comfort
- What is the most effective laser hair removal method? Find the Perfect Match for Your Skin & Hair
- Which is safer, diode or IPL? Discover the Safer Choice for Hair Removal
- Which is more effective, diode or IPL? The Definitive Answer for Permanent Hair Reduction