Yes, a YAG laser is a well-established and highly effective tool for welding. Specifically, the Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Nd:YAG) laser is a popular choice for many welding applications. Its ability to deliver high peak power in short pulses makes it ideal for creating precise, strong welds with minimal heat distortion to the surrounding material.
The core decision is not if a YAG laser can weld, but when it is the superior choice. Its unique ability to provide high-energy pulses gives it an advantage in precision spot welding and situations with imperfect part fit-up, even as newer technologies emerge.
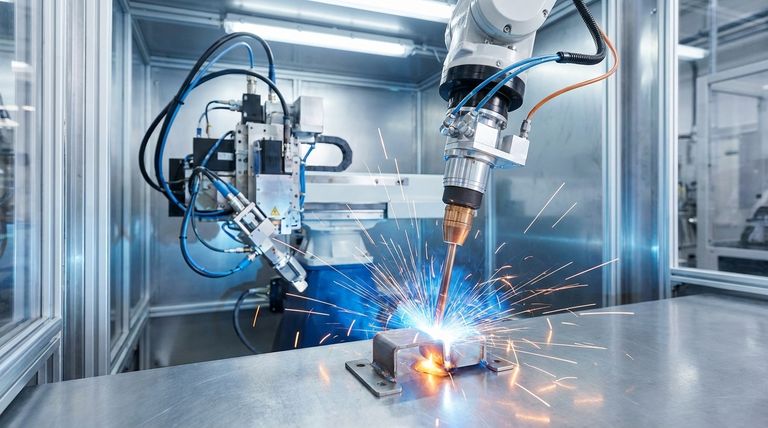

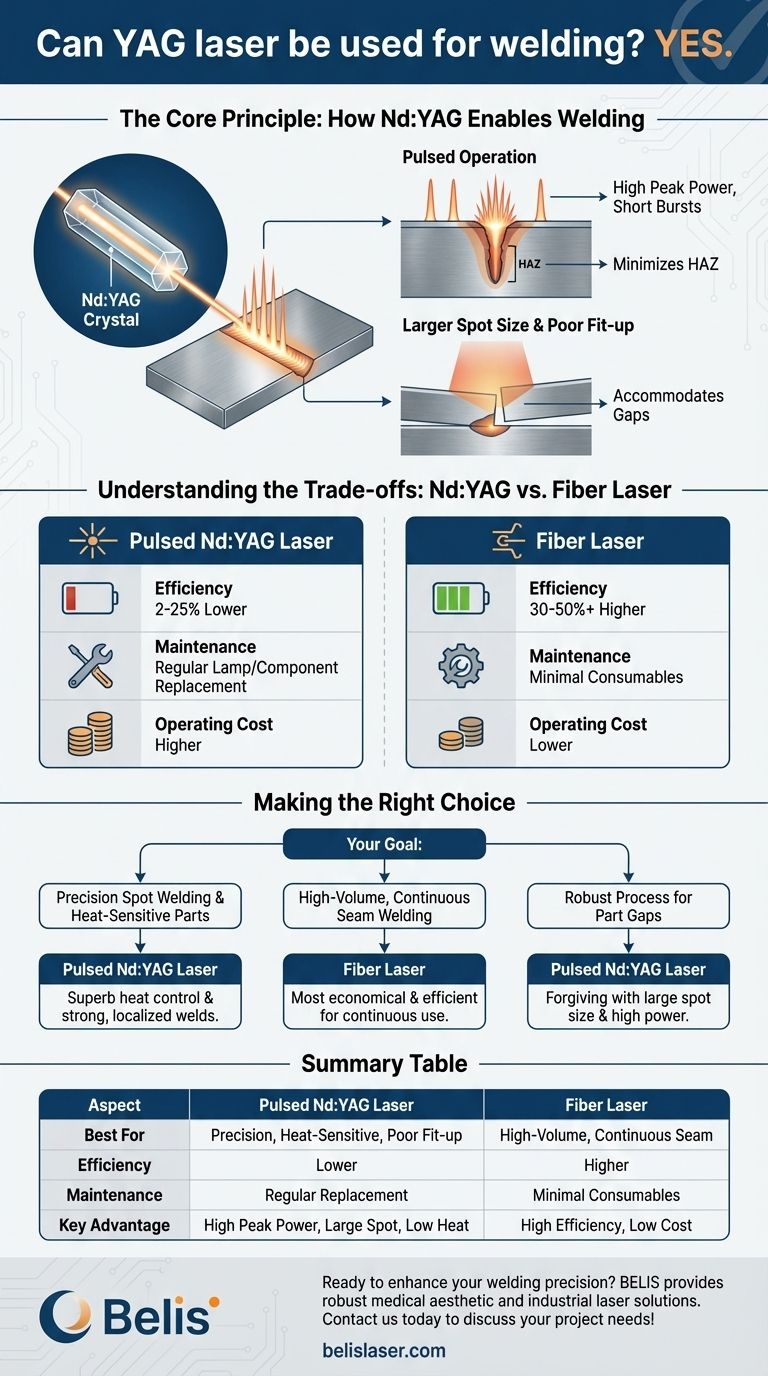
The Core Principle: How Nd:YAG Lasers Enable Welding
To understand why Nd:YAG lasers are used for welding, we need to look at how they deliver energy to the workpiece. The process is fundamentally different from a continuous beam.
The Role of the YAG Crystal
The term "Nd:YAG" refers to the laser's gain medium: a Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG) crystal that has been "doped" with Neodymium (Nd) ions. When this crystal is excited by a high-intensity lamp or laser diodes, it produces laser light at a 1064nm wavelength, which is highly effective for processing metals.
High Peak Power in Pulsed Operation
The key advantage of many Nd:YAG systems is their ability to operate in a pulsed mode. Instead of a steady stream of energy, the laser delivers extremely high power in very short bursts.
This high peak power instantly melts and vaporizes a small amount of material, forming a keyhole that allows the weld to penetrate deeply. Because the pulse is so short, the total heat input into the part remains low, minimizing the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ).
Accommodating Part Fit-up with Larger Spot Sizes
Pulsed Nd:YAG lasers can achieve high power density even with a relatively large optical spot size. This is a significant practical advantage.
A larger spot can bridge minor gaps or misalignments between the parts being welded, a common issue known as poor part fit-up. This makes the process more tolerant of real-world manufacturing variations without sacrificing weld quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful and versatile, the Nd:YAG laser is a mature technology. A modern technical evaluation must compare it to the current industry standard for many applications: the fiber laser.
Efficiency and Operating Costs
Traditional lamp-pumped Nd:YAG lasers are notoriously inefficient, often converting only 2-3% of electrical energy into laser light. The rest is lost as heat, requiring substantial cooling systems.
Diode-pumped Nd:YAG lasers are more efficient (10-25%), but both are generally surpassed by fiber lasers, which can reach efficiencies of 30-50% or more. This translates directly to lower electricity and cooling costs for fiber laser systems.
Maintenance and Consumables
Lamp-pumped Nd:YAG systems require regular replacement of flashlamps and other optical components, which represents a recurring maintenance cost and downtime.
Fiber lasers, being solid-state with no consumable parts in the laser source itself, offer significantly longer operational lifetimes and drastically reduced maintenance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct laser technology depends entirely on the specific requirements of your welding task.
- If your primary focus is precision spot welding or joining heat-sensitive components: A pulsed Nd:YAG laser is an excellent choice due to its superb control over heat input and its ability to create strong, localized welds.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous seam welding with low operating cost: A fiber laser is almost certainly the more economical and efficient solution in the long run.
- If your primary focus is a robust process tolerant of part gaps: The Nd:YAG laser's ability to operate with a larger spot size while maintaining high power makes it a very forgiving and effective tool.
Ultimately, understanding the unique strengths of each technology is the key to making an informed and effective decision for your project.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser | Fiber Laser |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Precision spot welding, heat-sensitive parts, poor fit-up | High-volume, continuous seam welding |
| Efficiency | Lower (2-25%) | Higher (30-50%+) |
| Maintenance | Regular lamp/component replacement | Minimal consumables, longer lifetime |
| Key Advantage | High peak power, large spot size, low heat input | High efficiency, low operating cost |
Ready to enhance your welding precision? BELIS specializes in professional medical aesthetic and industrial laser equipment, delivering robust solutions for clinics and premium beauty salons. Our expertise ensures you get the right technology for strong, reliable results. Contact us today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Q Switch Nd Yag Laser Machine Tattoo Removal Nd Yag Machine
- Clinic Use IPL and SHR Hair Removal Machine with Nd Yag Laser Tattoo Removal
- Pico Picosecond Laser Machine for Tattoo Removal Picosure Pico Laser
- Pico Laser Tattoo Removal Machine Picosure Picosecond Laser Machine
- Diode Laser SHR Trilaser Hair Removal Machine for Clinic Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using Nd:YAG lasers? Discover Versatility for Safe Skin Care & Precision
- Why is the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser essential for treating PIH? The Gold Standard for Safe Pigment Removal
- How does the Nd:YAG laser work? Unlocking Deep-Tissue Precision for Medical Aesthetics
- What types of pigmented lesions can an Nd:YAG laser treat? Expert Skin Solutions for Clinics
- What are the technical considerations for utilizing a 40 ms pulse width? Optimize Long-pulsed Nd:YAG Laser Safety



















